What Are Male Sexual Problems?
Problems with sexual functioning are common, affecting more than half of all couples at some time. Although sexual dysfunction rarely threatens physical health, it can take a heavy psychological toll, bringing on depression, anxiety, and debilitating feelings of inadequacy. Male sexual problems, particularly erectile dysfunction, may suggest an increased risk of vascular disease, so tell your doctor about it.
The major categories of sexual dysfunction in men include:
- Erectile dysfunction. Sometimes called impotence, it is the inability to have or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual functioning.
- Premature ejaculation. An inability to delay orgasm and ejaculation, such that it occurs very early in the course of sexual contact, leaving the other partner dissatisfied.
- Male orgasmic disorder. An inability to reach orgasm (climax) with a partner; or the inability to achieve orgasm without lengthy sexual contact; or the inability to have an orgasm during intercourse. In some cases, orgasm can be achieved only through masturbation or oral sex.
- Inhibited or hypoactive sexual desire. A disinterest in sexual contact or complete lack of sexual desire.
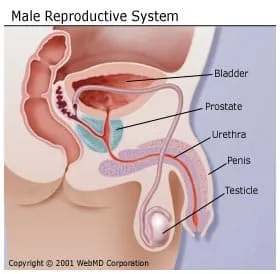
- Retrograde ejaculation. The semen, rather than emerging from the end of the penis, moves backward into the bladder during orgasm. This isn't dangerous. It is often a side effect of taking certain medications.
- Priapism. A prolonged erection unaccompanied by sexual desire; this rare condition is painful, potentially dangerous, and requires immediate medical attention. Call your doctor.
If your sexual problem only happens under a particular set of circumstances, or only with certain sexual partners, then your condition is considered to be "situational" rather than "generalized" (happening regardless of the circumstances or partner).
Many of these sexual conditions will happen at some point during the course of a man's life. In fact, some researchers only consider a diagnosis of sexual dysfunction if the problem occurs in 25% of all attempted sexual encounters.
What Causes Male Sexual Problems?
Because the sexual response is so complex, involving multiple factors, there are many causes of sexual dysfunction including physical and psychological causes.
An erection involves the nervous and vascular systems (the network of arteries and veins) and appropriate levels of hormones, so problems with any of these systems can interfere with sexual functioning.
Common physical causes of sexual problems include the following:
- Conditions or behaviors that increase the risk of vascular disease, such as smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity, or the medications to treat these and other disorders
- Diabetes, especially if you have type 2 diabetes
- Hypogonadism, in which the testicles do not produce enough testosterone
- Thyroid disorders(both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism)
- Adrenal lesions (Cushing's syndrome)
- Noncancerous pituitary growths that increase levels of a hormone called prolactin
- Diseases that affect the nervous system, including strokes, spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, long-standing diabetes, and Parkinson's disease
- Damage to arteries or veins following pelvic surgery (such as prostate, colon, or bladder surgery) or after radiation treatment
- Conditions that affect the penis directly, such as Peyronie's disease (penile curvature) or injury to the penis itself or to the arteries, veins, or nerves that supply the penis
- Cardiovascular (heart) disease
- Blockages in the blood flow to the penis (usually due to injury)
- Leaky veins
Premature ejaculation (PE) is usually not due to physical causes, although the problem is sometimes linked to a neurological disorder, prostate infections, or urethritis.
Possible psychological causes of sexual dysfunction include:
- Anxiety
- Guilty feelings about sex
- Sexual aversion disorder
- Learned behavior pattern of rapid ejaculation seen with frequent masturbation or infrequent sexual activity
Painful intercourse usually has physical causes such as these:
- An infection of the prostate, urethra, or testes, which can be initiated by sexually transmitted diseases, such as chlamydia and genital herpes
- An allergic reaction to spermicide or condoms
- Peyronie's disease, fibrous plaques on the upper side of the penis that often produce a painful bend during erection
- Arthritis of the lower back
Lack of sexual desire may be due to any of these factors:
- Physical illness
- Hormonal abnormality (usually low testosterone levels)
- Medications that affect libido
- Alcohol or recreational drug abuse
- Psychological causes, including depression or relationship problems, which a therapist may help identify
Retrograde ejaculation may occur in men from these causes:
- Prostate or urethral surgery
- Medication that keeps the bladder neck open
- Diabetes (which can injure the nerves that normally close the bladder during ejaculation)
Priapismmay be caused by:
- Penile trauma
- Medical conditions such as sickle cell disease, leukemia, gout, diabetes
- Certain medications, including those used to treat erectile dysfunction
Can Medication Cause Sexual Problems?
Many medications have been implicated in sexual dysfunction, causing inhibited sexual desire and/or erectile dysfunction, such as:
- Drugs to treat high blood pressure
- Diuretics (including thiazides and spironolactone)
- Histamine blockers
- Antidepressant medications
- Common over-the-counter preparations (particularly antihistamines and decongestants)
- Antipsychotic medications
- Sedatives
- Medications used to treat anxiety
- Use of drugs, including alcohol, methadone and heroin, anabolic steroids, and tobacco
Psychological Factors in Sexual Problems
Psychological factors play an important role. You may find it difficult to enjoy a sexual relationship if:
- You are under a lot of stress
- Your relationship is troubled
- You have a history of traumatic sexual encounters (rape or incest)
- You were raised in a family with strict sexual taboos
- You're afraid of getting your partner pregnant or of contracting a sexually-transmitted disease
- You have negative feelings (including guilt, anger, fear, low self-esteem, and anxiety)
- You are depressed
- You are severely fatigued
- You are pushing yourself to have sexual relations with someone you are not attracted to sexually
- Gender dysphoria issues.
Environmental Factors in Sexual Problems
You may find it difficult to enjoy sex if there is no safe, private place to relax and allow yourself to become sexual, or if fatigue due to an overly busy work and personal life robs you of the energy to participate sexually. Parents may find it difficult to find the time to be sexually intimate, given the demands/presence of their children.
Fear of contracting HIV (human immunodeficiency virus, which can lead to AIDS), the difficulties of striving for "safer sex," and the psychological effects of discrimination are just a few of the factors that can cause anxieties for men.

