What Are Pomegranates?
A pomegranate is a sweet, tart fruit with thick, red skin. While the skin is not edible, it holds hundreds of juicy seeds that you can eat plain or sprinkle on salads, oatmeal, hummus, and other dishes.
People have enjoyed pomegranates since ancient times for their health benefits. Modern research has found that the antioxidants in pomegranates can help protect your heart. The anti-inflammatory and antitumor properties of pomegranates may have promising use in cancer treatment and prevention, but more research is needed to prove this.
The most common way to enjoy a pomegranate is to cut it open and pull apart the skin to reveal the edible seeds and juice sacs, which are called arils.
Pomegranates grow on tall shrubs. These shrubs need ample heat to grow and ripen these delicious fruits. Pomegranates are native to Iran and northern India, but they also grow in the U.S. The majority of pomegranates are grown in California.
Pomegranate pronunciation
Pomegranate is pronounced as “paa·muh·gra·nuht.”
Pomegranate season
Pomegranates are in season from September to November, but their long shelf life means you can usually find them in grocery stores until January. You can find pomegranate juice year-round, though.
Pomegranate Seeds
The word pomegranate comes from the Latin phrase pomum grantum, which loosely means “apple of many seeds.” It's a fitting name as underneath their leathery skin, pomegranates are divided into several chambers, each filled with hundreds of red seeds.
Botanically, these seeds are called arils. An aril is the fleshy, transparent tissue that covers the pomegranate seed. When this skin is broken, the seeds release a red, juicy pulp.
Can you eat pomegranate seeds?
Though the peel of the fruit isn't edible, you can juice or eat pomegranate seeds whole in salads, cereal, and yogurt.
How to Open a Pomegranate
To open a pomegranate, first cut off both ends. You may see the membranes that divide the inside of the fruit. Cut into the skin from top to bottom along these ridges.
Next, slice deep enough to cut through the skin and the white membrane without cutting the pomegranate seeds. Hold the pomegranate over a bowl of water and pry it apart with your fingers.
Pull the seeds away from the membrane and skin, allowing them to fall into the bowl of water. The membrane will float to the top of the water, and the seeds will sink to the bottom. Remove the membrane, and throw it away. Drain the water from the seeds.
What Is Pomegranate Juice?
You can remove the seeds of a pomegranate and press them to release the juice of the fruit. Pomegranate juice is especially common in Iran, but other countries enjoy it as well. Bottled pomegranate juice is an easy way to enjoy some of the health benefits of this delicious fruit.
How to make pomegranate juice
You can press the seeds from a pomegranate into juice. A large pomegranate will yield between 1/4 and 1/2 cup of juice.
To extract the juice, crush the seeds in a food mill or sieve. You can also blend the seeds, then pour the liquified mixture through a strainer to remove any leftover pulp from the juice.
You can freeze or can pomegranate juice to make it last longer. If you choose to can it, add a few tablespoons of lemon juice to it before sealing the can to maintain the juice's vibrant color.
Pomegranate Tea
Pomegranate tea is made with crushed pomegranate seeds, dried pomegranate flowers, or by adding pomegranate juice concentrate to tea.
You can buy or grow pomegranates and make this tea yourself or purchase it at most grocery stores in the tea section. If you buy it pre-made, you’ll often find it mixed with mint, black tea, or green tea.
Pomegranate tea nutrition
One cup of brewed pomegranate tea contains:
- Calories: 6
- Protein: 0 grams
- Fat: 0 grams
- Carbohydrates: 1 gram
- Fiber: 0 grams
- Sugar: 0 grams
Pomegranate juice and tea are rich in nutrients. Two compounds present in pomegranate seeds—punicalagins and punicic acid—are highly potent antioxidants.
Other Pomegranate Drinks
Pomegranate juice can brighten any cocktail, including:
Pomegranate martini
Add pomegranate juice, vodka, Cointreau liquor, sparkling water, and a squeeze of lemon to an ice-filled martini shaker. Combine and serve in a chilled martini glass.
Pomegranate margarita
Mix together tequila, pomegranate juice, lime juice, agave, and salt in an ice-filled cocktail shaker. Strain the mixture into a tumbler filled with ice and enjoy.
Leave out the alcohol for a delicious mocktail version of either drink.
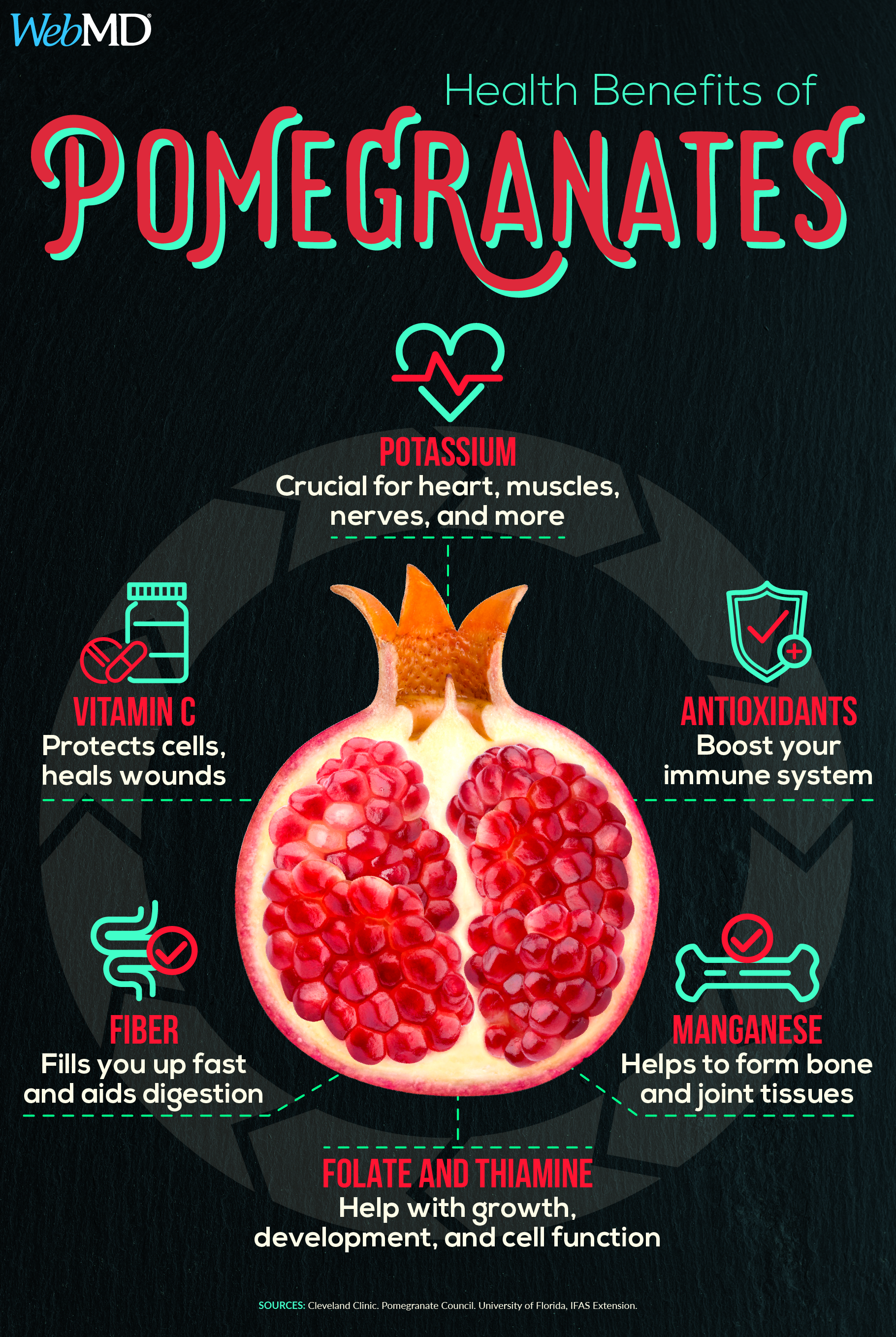
Pomegranate Benefits
Pomegranates can have up to three times more antioxidants than green tea or red wine. Antioxidants protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals and reduce inflammation.
Other health benefits of pomegranates include the following:
Better heart health
Studies suggest that pomegranates can help protect your heart in many ways, such as lowering blood pressure as well as blood sugar levels. Pomegranates have polyphenol compounds called punicalagins or ellagitannins. These antioxidants help prevent your artery walls from thickening and lower the buildup of cholesterol and plaque. Pomegranate juice also has high amounts of plant pigments called anthocyanins and anthoxanthins, which support good heart health.
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of cholesterol and fats in the arteries, is a common cause of heart disease. Pomegranate juice may help reduce LDL cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, which clogs arteries. It can also increase HDL cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol, which lowers the risk of stroke and heart attack.
Improved diabetes control
Early studies have suggested that people with type 2 diabetes who began to drink pomegranate juice showed an improvement in insulin resistance, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Possible lowered risk of cancer
Pomegranates are rich in antioxidantsand flavonoids, both of which help prevent free radicals from damaging your cells. In some early studies, pomegranates show potential in helping prevent prostate, breast, lung, and colon cancers. Additionally, preclinical studies on animals have shown that eating pomegranates may help inhibit the growth of lung, skin, colon, and prostate tumors. More research is needed to better understand these effects on humans.
Pomegranate Nutrition
Fresh pomegranate is a source of fiber, which can promote weight loss, lower cholesterol, and ease constipation.
Nutrients per serving
Half of a pomegranate, which equals one serving, contains:
- Calories: 72
- Protein: 2.35 grams
- Fat: 1.6 grams
- Carbohydrates: 26 grams
- Fiber: 5.5 grams
- Sugar: 20 grams
An 8-oz serving of pomegranate juice contains:
- Calories: 135
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: 0 grams
- Carbohydrates: 34 grams
- Fiber: 1 gram
- Sugar: 30 grams
- Sodium: 10 grams
While pomegranates lose much of their vitamin C content when juiced, they retain nearly all of their potassium, about 536 mg. Potassium is an important mineral that helps your nerves and heart stay strong. Enjoying fresh pomegranates or their juice gives you plenty of this key mineral.
Some pomegranate-flavored drinks have more calories because they contain more sugar than plain pomegranate juice. To get the health benefits of pomegranates without the extra calories, look for bottles that say “100% juice.”
Potential Risks of Pomegranate and Pomegranate Juice
Pomegranates are typically safe to eat. But some people may get unwanted side effects. An allergic reaction to pomegranate is rare but can happen. If you have an allergy to plants, watch for possible symptoms, which can include hives or troubled breathing.
Pomegranate can also interact with some drugs and medications. You may want to check with your doctor or limit your consumption of pomegranate if you're taking such medications as:
- ACE inhibitors or other drugs for high blood pressure
- Crestor and other drugs for high cholesterol that can break down in your liver
- Blood thinners such as warfarin (Coumadin)
How to Eat Pomegranate
You can easily add pomegranate into your diet by:
- Adding the seeds to a quinoa salad with other fresh fruits and vegetables
- Sprinkling pomegranate seeds onto your yogurt with granola to make a parfait
- Giving your salad a pop by adding pomegranate seeds
- Blending pomegranate juice with bananas and yogurt to make a smoothie
- Mixing pomegranate juice, rice vinegar, oil, garlic, and white sugar to make a salad dressing
Pomegranate molasses
Pomegranate molasses is a syrup made by boiling down pomegranate juice, sometimes with added lemon juice and sugar. It can be used to marinate meat or to make salad dressings. Pomegranate molasses is a popular ingredient in West Asian cooking.
Growing Pomegranates
Pomegranates grow on dense, multi-trunked shrubs. Sometimes these shrubs can be pruned into single-trunked trees. The branches of these shrubs are thorny with dark green, oval-shaped leaves. They can grow up to 10-12 feet tall.
How to grow pomegranates
Pomegranates grow best in warm climates that have temperatures over 85 F (29 C) for at least 120 days a year. The shrub thrives in loamy, well-drained soil and should be planted in an area that gets at least 6 hours of direct sunlight every day.
If you want to grow your own pomegranate shrub, it's best to start with a hardwood cutting or a branch of a larger pomegranate shrub that has been trimmed after shedding its leaves for the winter. Make the cutting in late fall or early winter, and plant it in a pot. By the following spring, transplant the cutting into the ground.
In a few years, your pomegranate shrub will reach maturity, and it will flower and then bear fruit. Pomegranates are typically harvested between August and November. Let the fruit ripen for as long as possible on the tree, because pomegranates won't continue to ripen after they're picked. While harvesting pomegranates, cut as close to the fruit as you can, and handle the fruit gently to avoid puncturing the skin.


