Arthroscopy for Knee Pain
Hide Video Transcript
Video Transcript
[MUSIC PLAYING]
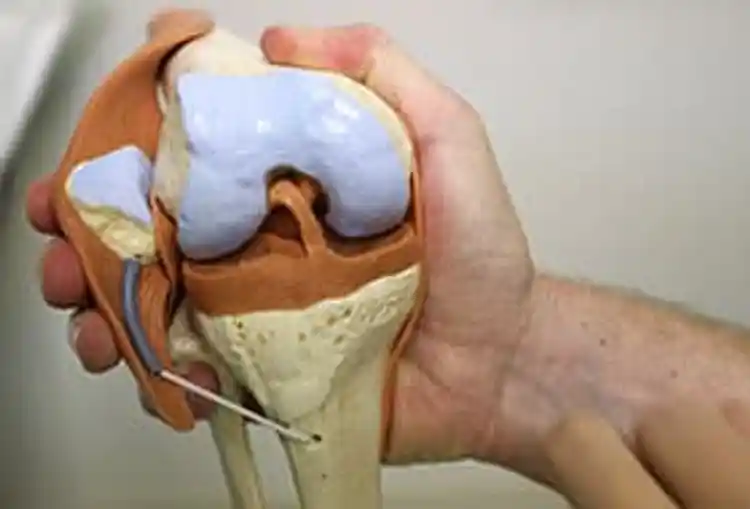
THOMAS MYERS: So with the patient under anesthetic, we can make two small incisions in the front of the knee. There's an initial incision here for the camera, which is a small poke hole. Camera's then inserted into the knee joint, and a second poke hole was made on this side of the kneecap. And then we bend the knee and open the knee up with the camera and the instruments in place, and we perform what's called a 15-point diagnostic arthroscopy. That allows us to look in every nook and cranny inside the knee and make the diagnosis.
Preparing for arthroscopy is not that difficult. You need to make sure that you stop medications that might thin your blood and cause bleeding. You need to have a conversation with your doctor as to whether a pre-operative examination by your primary care doctor is required. If you have underlying medical conditions, those issues need to be addressed prior to surgery.
No changes in your health otherwise? You're not sick now, you're not on any antibiotics now.
You're going to have to take pain medication for two to three days post operatively. You're going to have to take an anti-inflammatory medication, one a day for 30 days after surgery for inflammation and swelling. So incisions look good?
The success rate for arthroscopy is in the high 90th percentile, depending on the diagnosis.
How about where the meniscus tear was? Are you sore in here at all?
THOMAS MYERS
Arthroscopy provides unparalleled access to all parts of the joint. It makes surgery that was typically incredibly difficult easy. It's less invasive. There's less bleeding. It hurts less. It allows us to perform incredibly complicated procedures through tiny incisions. The most common thing we treat with arthroscopy are meniscal injuries, tears of the meniscus. KEITH MASTERS
When I tore my meniscus, it felt like someone had stuck an ice pick right in the side of my knee, and every step after that felt like that ice pick was there. THOMAS MYERS: So with the patient under anesthetic, we can make two small incisions in the front of the knee. There's an initial incision here for the camera, which is a small poke hole. Camera's then inserted into the knee joint, and a second poke hole was made on this side of the kneecap. And then we bend the knee and open the knee up with the camera and the instruments in place, and we perform what's called a 15-point diagnostic arthroscopy. That allows us to look in every nook and cranny inside the knee and make the diagnosis.
KEITH MASTERS
He makes two incisions, one for the camera, one for the tools, and just simply takes a sharp knife and just cuts the tear out, very clean. THOMAS MYERS
There are some limitations with the arthroscope, but basically, we can get into the knee, we can trim out loose tissue, we can remove torn edges of the meniscus, we can smooth cartilage, we can treat arthritis, we can remove loose fragments of bone or cartilage, we can sew tissues together, and we can even reconstruct an entire ligament. Preparing for arthroscopy is not that difficult. You need to make sure that you stop medications that might thin your blood and cause bleeding. You need to have a conversation with your doctor as to whether a pre-operative examination by your primary care doctor is required. If you have underlying medical conditions, those issues need to be addressed prior to surgery.
No changes in your health otherwise? You're not sick now, you're not on any antibiotics now.
SUBJECT 1
No. THOMAS MYERS
You haven't started any new medications since we talked last. A knee scope is really minimally invasive. You'll be back on your feet in a couple days. You're going to need to elevate your knee. You're going to need to use ice intermittently for swelling. Typically, you can weight bear on the knee within 48 hours of the operation. You're going to have to take pain medication for two to three days post operatively. You're going to have to take an anti-inflammatory medication, one a day for 30 days after surgery for inflammation and swelling. So incisions look good?
KEITH MASTERS
The recovery time is the main thing. He's always trying to look at what your lifestyle is and trying to get you back to that as soon as possible. THOMAS MYERS
Typically, full recovery and return to sport is about six weeks with good physical therapy. Don't neglect strength training in your legs. The success rate for arthroscopy is in the high 90th percentile, depending on the diagnosis.
How about where the meniscus tear was? Are you sore in here at all?
SUBJECT 2
No. THOMAS MYERS
So that's all gone? SUBJECT 2
That feels sort of better. THOMAS MYERS
Arthroscopy's one of the biggest advances in orthopedic surgery in the last few decades.