Creatures That Live on Your Body
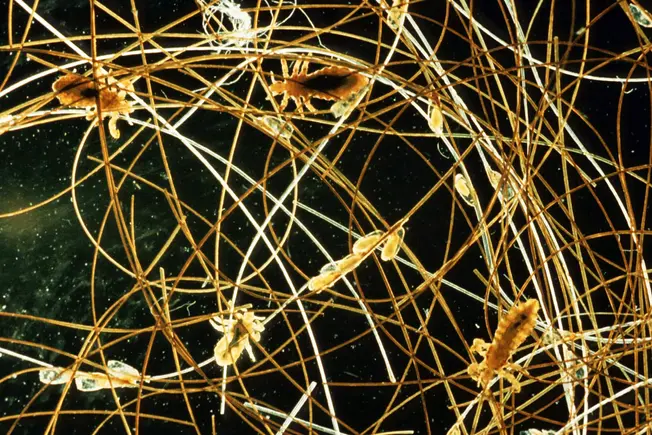


Head Lice
These tiny insects can live in your hair and drink blood from your scalp. They’re generally not dangerous, just itchy and contagious. They’re common in elementary school kids. You can buy shampoos over the counter that kill them, and your doctor can tell you about prescription ones. You’ll need to use a wet fine-tooth comb (called a nit comb) on your hair to get rid of them.
Even if you do, they can lay eggs, too. If they hatch, you’ll itch all over again.
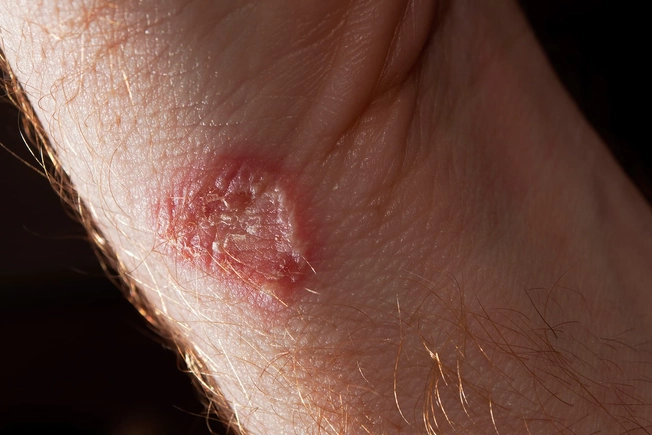
Ringworm
Don’t worry. It’s not really a worm at all. It’s a fungus that can infect just about any part of your body. On your head, it could cause hair to fall out in the distinct ring pattern that gives it its name. On your feet, it’s called athlete’s foot, and in your crotch area, it’s jock itch.
Your doctor or pharmacist can help you get rid of it with antifungal creams, sprays, powders, or pills.
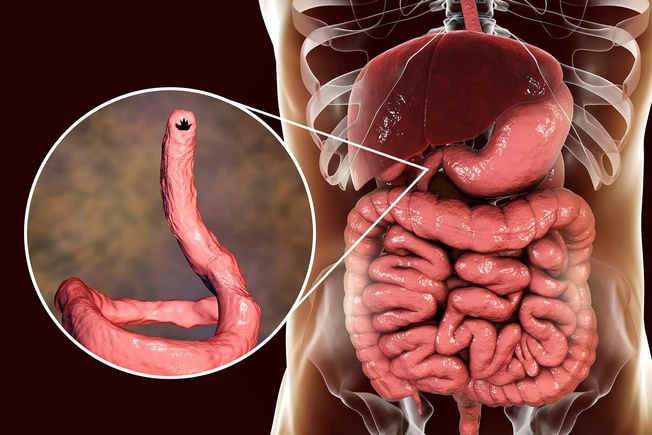
Hookworm
This is rare in the U.S., but hookworm larvae -- usually found in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East -- can enter your skin, often when you walk barefoot on soil that has infected poop. They live in your gut, aren’t generally dangerous, and often go away without treatment.
The creature can make you itchy and red where it went into your skin. You may also cough, wheeze, and have stomach pain.
Talk to your doctor if you think you have it.
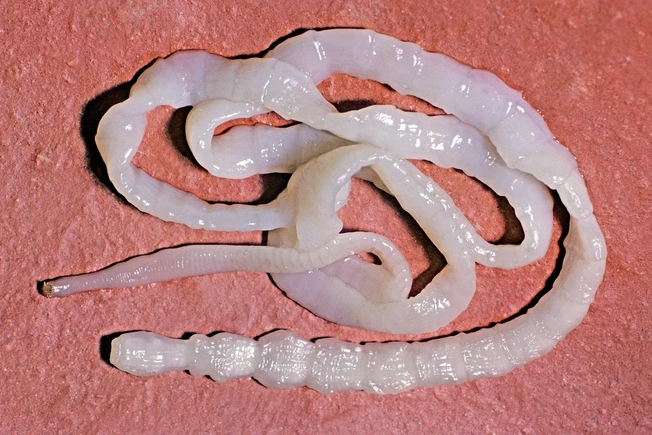
Tapeworm
You can get this parasite from infected beef, pork, or fish. If you have it, you’ll probably see tiny eggs and pieces of the worm in your poop.
A worm can grow to 30 feet long inside you and cause diarrhea, cramps, and weight loss.
Your doctor can give you drugs to get rid of it. Early treatment is important because it could lead to brain cysts that can cause headaches, seizures, and confusion. It can also bring life-threatening disease.
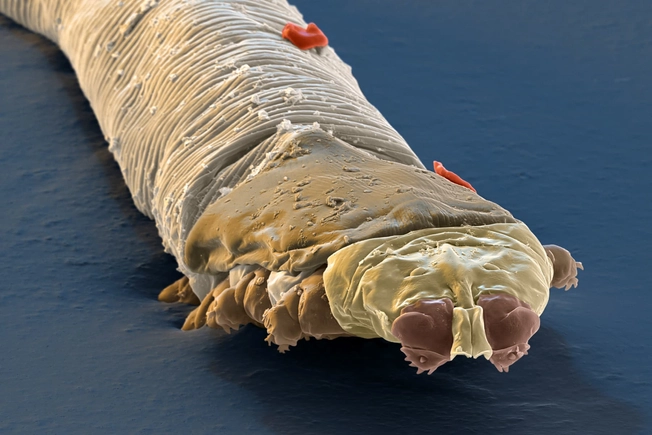
Face Mites
Also known as demodex, they’re basically tiny spiders you pick up as you age. By age 60, you’ve got a couple of thousand of the little guys living on your face. You can’t see them because they’re only about a third of a millimeter long and see-through.
They’re not anything to worry about. All they want is to eat some dead skin cells and a bit of the oil that comes along with them.
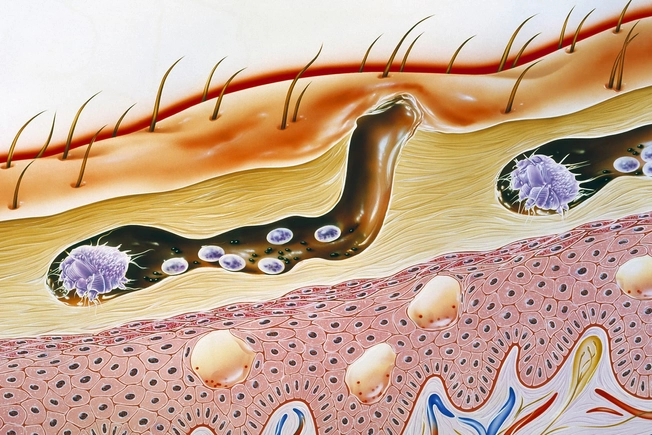
Scabies
The aptly named “human itch mite” uses its eight legs to burrow into the top layer of your skin to feed in your groin, armpits, between your fingers or toes, or under your belt.
Your body responds with an itchy rash. You might get it from another person if you touch their skin, or from sheets, clothes, or furniture. Your doctor can tell if you have it, and prescription drugs can get rid of it. Wash bedding and clothes to finish the job.
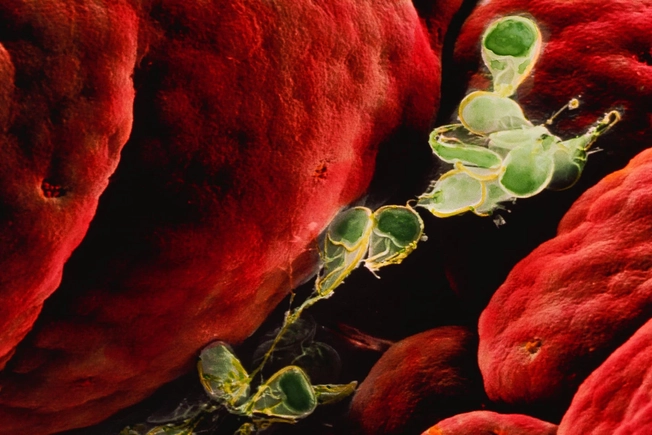
Giardia
These are tiny little parasites that live in your gut. You can get them if you swim or drink from some streams and lakes. You might also get them from hot tubs, well water, swimming pools, contaminated food, and contact with an infected person. Giardia can give you cramps, gas, weight loss, sulfur-smelling burps, and foul-smelling diarrhea. Then again, you may not have any symptoms. |
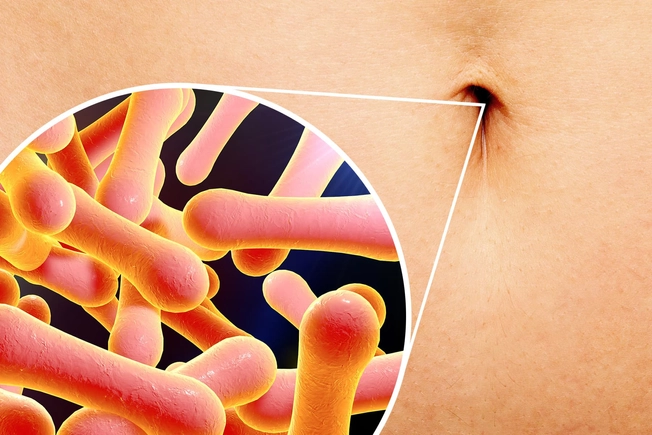
Bellybutton Bacteria
In the folds of your navel, glands make sweat, oil, and other things that attract some bacteria and repel others. Some of these might make you sick in other places. But here, they could help fight off more dangerous germs. Things like your gender, your body makeup, where you live, and your genes can determine which bacteria -- and how much of it -- you’ll have.
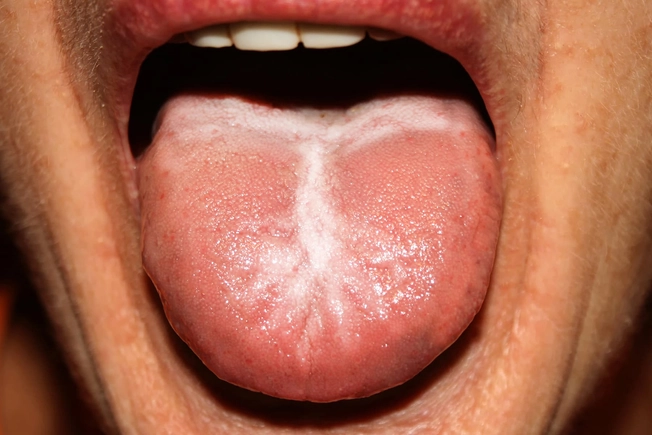
Candida: The Fungus Among Us
This thrives in dark, warm, moist places like your mouth, the folds of your skin, and your crotch. It causes a rash of dry, itchy, swollen skin. In your mouth, it could grow too much and cause patches of itchy white bumps on your tongue, throat, or inside your cheeks. You may hear your doctor call that “thrush.” It can be treated with antifungal drugs.
In adults this condition is rare. When it does occur, it's usually associated with immunocompromise from: AIDs, chemotherapy, uncontrolled diabetes, or improper use of inhaled steroids.
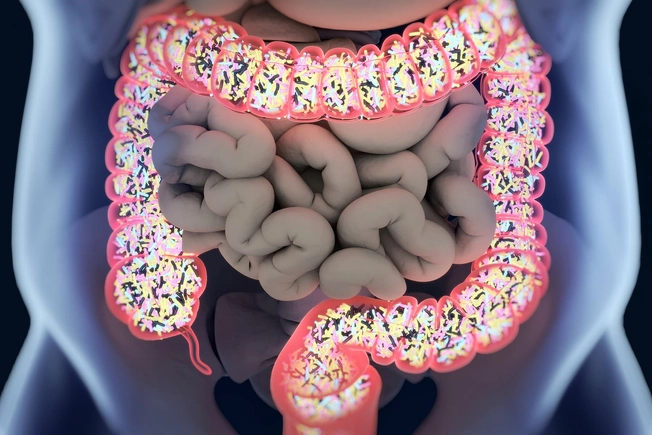
Gut Microbiome
Most of the trillions of microscopic things that live in and on your body are inside your gut. They interact with your diet, your body, and the outside environment. Researchers are still figuring out how.
Everyone has a gut microbiome. You could have a healthy microbiome or a less healthy one, and you can manipulate both with diet, antibiotics, and even stool transplants with the supervision of your doctor.
Mouth Creatures
A delicate balance of bacteria, fungi, and viruses live in your mouth all the time. Problems like cavities or sores can start when that balance gets thrown off. This can happen because of things like dry mouth, diabetes, poor oral hygiene, or a weak immune system.
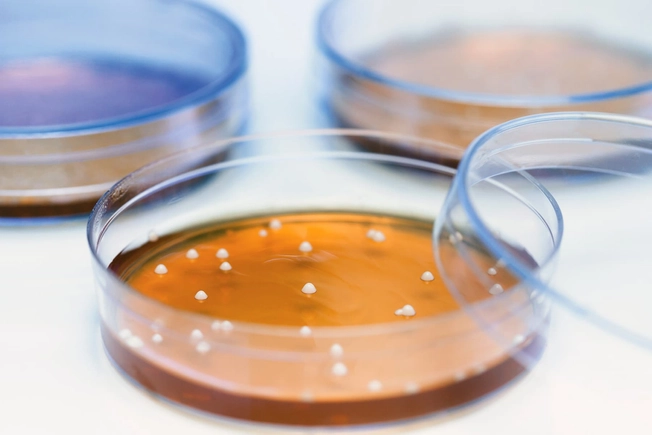

Lactobacilli bacteria
A fine balance and variety of microscopic creatures live inside the vagina. They’re thought to be the first line of defense against other microbes that could give you smelly vaginal discharge and itch. Lactobacilli bacteria, in particular, promote vaginal health because they help keep acid levels just right. This can help prevent bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections.
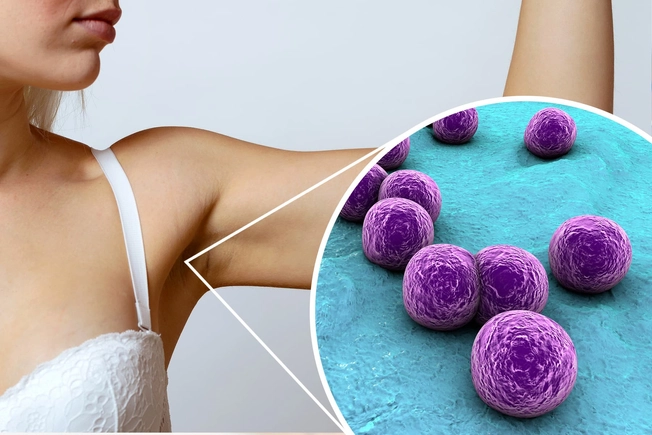
Armpit Microbiome
The balance of creatures in your mouth and gut aren’t the only ones that matter. Even your armpits have a microbiome that’s part of the reason for the odor that comes from there. The mix is often dominated by “staph” bacteria. But it can change drastically if you use antiperspirant.