Pneumonia is inflammation or swelling in the lungs in which the air sacs fill with pus and other fluids, making it difficult for oxygen to reach the blood. Pneumonia can be typical or atypical. Typical pneumonia is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as the pneumococcal pneumonia. Atypical pneumonia can be caused by viruses, fungi, bacteria, or chemicals (such as when stomach contents are inhaled into the lungs).
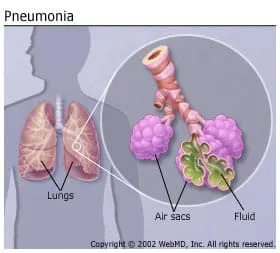
People who are otherwise healthy often recover quickly when given prompt and proper care. However, the elderly or those with chronic illnesses (such as Parkinson's disease) often develop a serious infection that needs prompt and often aggressive treatment in the hospital.
What Is Bacterial Pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia is pneumonia caused by bacteria. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia.
There is a vaccine available to protect people from this infection.
What Are the Symptoms of Bacterial Pneumonia?
Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia can develop gradually or suddenly. Symptoms include:
- High fever (up to 105 degrees)
- Drowsiness
- Rapid breathing
- Chills
- Cough with mucus (may be greenish or have blood)
- Chest pain
- Blue tint on lips or under the nails (severe cases)
Who Should Get the Pneumonia Vaccine?
You should get the pneumonia vaccine if you:
- Are over age 65
- Have a chronic illness, such as Parkinson's disease, diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease
- Have HIV or AIDS
- Have a weak immune system from another cause, such as from certain kidney diseases and some cancers, or have had your spleen removed
- Are taking drugs, such as prednisone, that weaken the immune system
What Is Viral Pneumonia?
Viral pneumonia is pneumonia caused by a virus. About half of all people with pneumonia have viral pneumonia. Viral pneumonia is usually less serious than bacterial pneumonia and can take from two to four weeks to recover.
What Are the Symptoms of Viral Pneumonia?
Early symptoms of viral pneumonia are similar to the flu, and include:
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle pain
Added symptoms that may occur about a day later include:
- High fever
- Cough with mucus
- Shortness of breath
Additional symptoms of severe cases can include:
- Extreme breathlessness
- Blue tint on lips or under the nails
How Can I Protect Myself From Pneumonia?
- Get a viral influenza (flu) vaccine (shot) each year. Flu vaccines are prepared annually in anticipation of that year's virus strain. Influenza can make pneumonia infection more likely.
- Get the pneumonia vaccine to protect yourself against Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Get Covid vaccines to protect against Covid-19.
- Get treated for any other infections in the respiratory system, especially those in the lungs.
- Wear a face mask and avoid exposure to people who may be sick with Covid-19, a flu, or a cold.
- Wash your hands before eating, before preparing food, and after going outside.
- Eat a healthy diet, exercise, and get plenty of rest.
- Contact your doctor if you think you have symptoms. Don't wait for symptoms to worsen, as you may develop an emergency condition.
- Don't smoke.
- Don't use alcohol heavily.
How Is Pneumonia Treated?
Bacterial pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics -- usually by mouth. For more severe pneumonia, you may need to go to the hospital to be treated. Hospital treatment may include oxygen therapy to increase oxygen in the blood, intravenous (given through a needle in your vein) antibiotics, and fluids. Pain relievers and medicine to reduce fever may also be given. With treatment, bacterial pneumonia usually begins to improve within 24-48 hours.
Viral pneumonia is usually less serious. A stay in the hospital is rarely needed. Antibiotics cannot be used to treat viral pneumonia, but may be given to fight a bacterial infection that is also present. Other drugs, such as those listed above, may be used to lessen symptoms. If you are given antibiotics, make sure you take all of the medicine, even if you feel better. If you stop taking the medicine too early, the infection can come back and may be harder to treat.
For both viral and bacterial pneumonia:
- Drink warm fluids to relieve coughing.
- Rest.
- Don't rush your recovery. It can take weeks to get your full strength back.
- Don't smoke.

