What Is Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia?
Hide Video Transcript
Video Transcript
[MUSIC PLAYING]
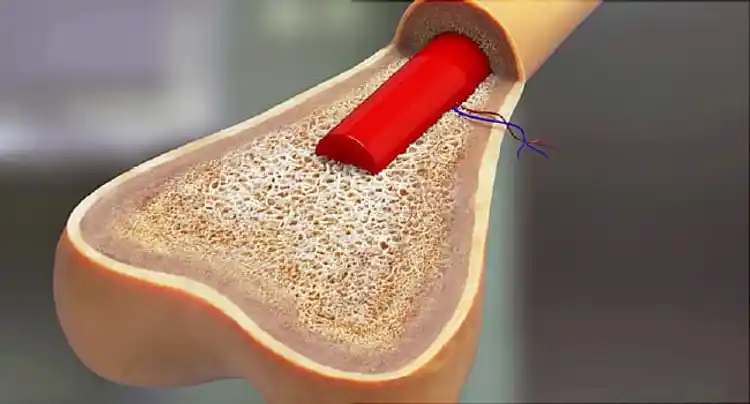
Normally, these cells help your body fight infection, but because of the change-- called a mutation-- faulty white blood cells that don't work like they should are made instead. These damaged blood cells build up in your bone marrow, crowding out healthy cells, and keeping new blood cells from being made. As they continue to grow, they can spread to your blood and build up in your organs.
CLL gets worse slowly, and many people don't have symptoms at first. Over time, you could have swollen lymph nodes, a fever, a tired feeling, belly pain, night sweats, weight loss, or more frequent infections. You're more likely to get CLL if you're middle-aged or older, have been around certain chemicals, or if a family member has had blood or bone cancer.
To see if you have chronic lymphocytic leukemia, your doctor will run some tests on your blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. If your CLL is in the early stages, you may not need treatment right away. If you do, your treatment will depend on your cancer stage, symptoms, total health, and preferences. Treatment options can include chemotherapy, targeted drugs, immunotherapy, and bone marrow transplant.
For more information about chronic lymphocytic leukemia, talk to your doctor. [MUSIC PLAYING]
SPEAKER
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia-- or CLL-- is a type of cancer that happens in your blood and bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside your bones. While the exact cause isn't known, doctors do know that something happens to change the genetic code inside your cells that make white blood cells. Normally, these cells help your body fight infection, but because of the change-- called a mutation-- faulty white blood cells that don't work like they should are made instead. These damaged blood cells build up in your bone marrow, crowding out healthy cells, and keeping new blood cells from being made. As they continue to grow, they can spread to your blood and build up in your organs.
CLL gets worse slowly, and many people don't have symptoms at first. Over time, you could have swollen lymph nodes, a fever, a tired feeling, belly pain, night sweats, weight loss, or more frequent infections. You're more likely to get CLL if you're middle-aged or older, have been around certain chemicals, or if a family member has had blood or bone cancer.
To see if you have chronic lymphocytic leukemia, your doctor will run some tests on your blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. If your CLL is in the early stages, you may not need treatment right away. If you do, your treatment will depend on your cancer stage, symptoms, total health, and preferences. Treatment options can include chemotherapy, targeted drugs, immunotherapy, and bone marrow transplant.
For more information about chronic lymphocytic leukemia, talk to your doctor. [MUSIC PLAYING]