Back Pain Myths

The Truth About Back Pain
It might be a sharp stab. It might be a dull ache. Sooner or later, 8 out of 10 of us will have back pain. And back pain myths are almost as common. Let's set the record straight about what you may have heard.
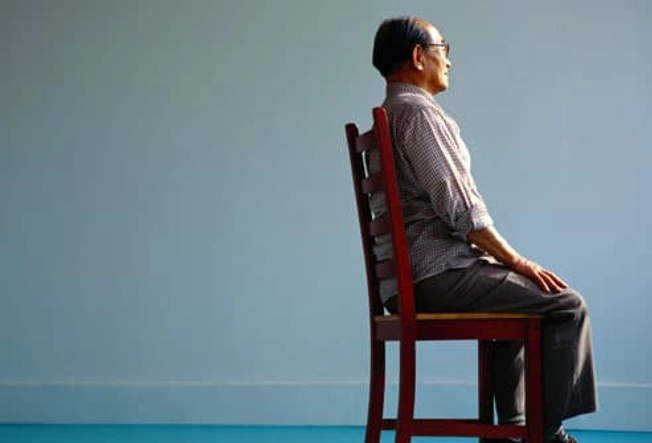

Myth: Always Sit Up Straight
Slouching is bad. But sitting up too straight and still for long periods can also be a strain on your back. Take breaks a few times a day: Lean back in your chair with your feet on the floor and let your back curve slightly. Even better: Try standing for part of the day, perhaps while you're on the phone or reading.
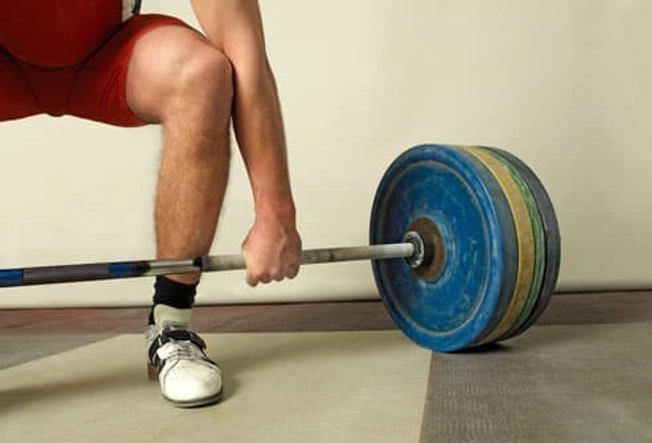

Myth: Don't Lift Heavy Things
It's not necessarily how much you lift, it's how you do it. Get directly in front of the object. Squat close to it, with your back straight and head up. Stand, using your legs to push up the load and your arms to hold it close to your middle. Don't twist or bend your body, or you may hurt your back. (Of course you shouldn't pick up anything that might be too heavy for you.)
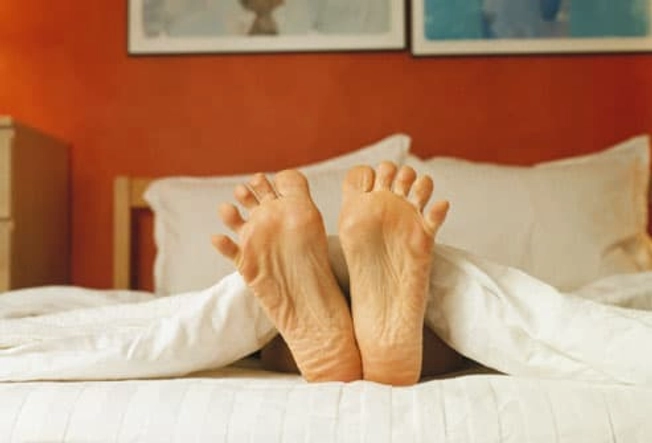

Myth: Bed Rest Is the Best Cure
Yes, resting can help a recent injury or strain that causes back pain. But a day or two in bed can actually make it worse.

Myth: Pain Is Caused by Injury
Disc degeneration, diseases, infections, and even inherited conditions can make your back hurt, too.

Fact: More Pounds, More Pain
Staying fit helps prevent back pain. As you might guess, extra pounds will put stress on your back. Back pain is most common among people who are out of shape, especially weekend warriors who push themselves hard after sitting around all week.

Myth: Skinny Means Pain-Free
Anyone can get back pain. People who are too thin, such as those with an eating disorder like anorexia, may have bone loss. They're more likely to get broken bones and crushed vertebrae.

Myth: Exercise Is Bad for Back Pain
This is a big one. Regular exercise prevents back pain. And doctors may recommend exercise for people who have recently hurt their lower back. They'll usually start with gentle movements and gradually build up the intensity. Once the immediate pain goes away, an exercise plan can help keep it from coming back.
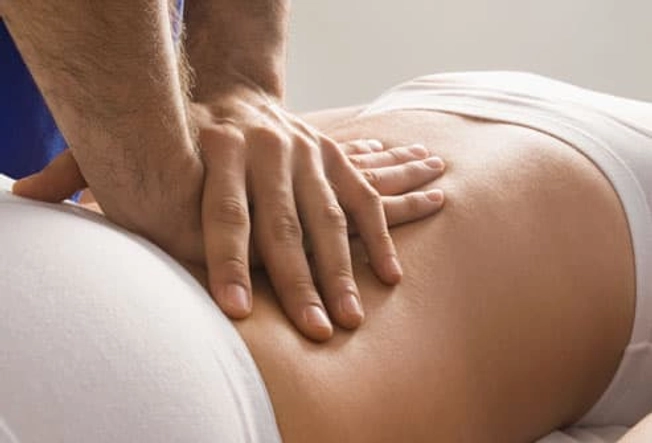

Fact: Chiropractic Care Can Help
Treatment guidelines from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society recommend that patients and doctors consider other options with proven benefits for low back pain. These include spinal manipulation and massage therapy.
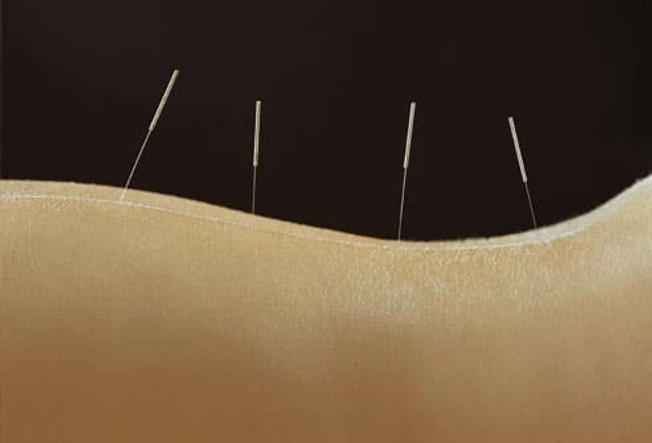
Fact: Acupuncture May Ease Pain
The same organizations say acupuncture, yoga, progressive relaxation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy may help when you don't get relief from standard self-care.

Myth: Firmer Mattresses Are Better
In a Spanish study, people with ongoing general back pain who slept on a medium-firm mattress hurt less and were able to move better than those who slept on a firm mattress. But one size doesn't fit all. Choose your mattress based on your sleep habits as well as the cause of your back pain.