Understanding Polycythemia Vera
Hide Video Transcript
Video Transcript
NARRATOR
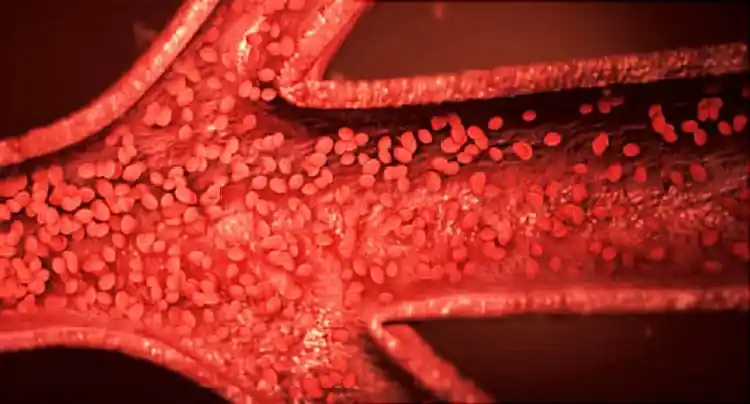
Polycythemia vera is a slow growing blood cancer that happens in your bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside bones. It's usually caused by a gene mutation. Your bone marrow makes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Normally, your body controls how many of each kind of these blood cells are made. But with polycythemia vera, your body makes too many red blood cells. It may also make too many white blood cells and platelets.
These extra cells thicken your blood and slow down its flow. Blood clots can form more easily, which can block the flow of blood through your blood vessels. This can cause a heart attack or stroke.
With slower blood flow, your body doesn't get the oxygen it needs to work the way it should. Because of this, you may have headaches, dizziness, itching, and vision problems. The lack of oxygen can also bring on chest pain and heart failure can happen.
Your spleen's job is to filter out old or damaged blood cells, but with too many red blood cells, your spleen can't do its job. This can cause it to swell, leading to pain, bleeding, and frequent infections.
Too many red blood cells can also cause inflammation in your joints, ulcers to form in your digestive tract, or kidney stones. Sometimes, polycythemia vera can lead to other serious blood diseases, too, by keeping your bone marrow from working altogether. For more information, talk to your doctor.
