What Is Brain Cancer?
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells in the brain.
- Although such growths are popularly called brain tumors, not all brain tumors are cancer. Cancer is a term reserved for malignant tumors.
- Malignant tumors can grow and spread aggressively, overpowering healthy cells by taking their space, blood, and nutrients. They can also spread to distant parts of the body. Like all cells of the body, tumor cells need blood and nutrients to survive.
- Tumors that don’t invade nearby tissue or spread to distant areas are called benign.
In general, a benign tumor is less serious than a malignant tumor. But a benign tumor can still cause problems in your brain by pressing on nearby tissue.
In the U.S., brain or nervous system tumors affect about 6 of every 1,000 people.
Primary Brain Cancers
The brain is made up of many different types of cells.
- Some brain cancers happen when one type of cell changes from its normal characteristics. Once transformed, the cells grow and multiply in abnormal ways.
- As these abnormal cells grow, they become a mass, or tumor.
- The brain tumors that result are called primary brain tumors because they start in your brain.
- The most common primary brain tumors are gliomas, meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, vestibular schwannomas, and primitive neuroectodermal tumors (medulloblastomas). The term glioma includes glioblastomas, astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas.
- Most of these are named after the part of the brain or the type of brain cell from which they arise.
Metastatic Brain Cancer
Metastatic brain tumors are made of cancerous cells from a tumor elsewhere in the body. The cells spread to your brain from another tumor in a process called metastasis. This is the most common type of brain tumor.
Causes of Brain Cancer
The exact cause of most brain cancer is unknown. Genetic factors, various environmental toxins, radiation to the head, HIV, and cigarette smoking have all been linked to cancers of the brain. In most cases, no clear cause can be shown.
Diagnosing Brain Cancer
Your doctor will start by asking questions and giving you a physical exam to see if you have a problem with your brain or brain stem.
They might do a CT scan of your brain. This test is like an X-ray but shows more detail in three dimensions. Usually, the doctor will inject a dye into your bloodstream to highlight problems on the scan.
If the doctor thinks you have a tumor, they’ll follow up with an MRI scan. You might also get routine lab tests to check for other medical problems. These include analysis of blood, electrolytes, and liver function tests. If your mental status has been a problem, they might do blood or urine tests to make sure drugs aren’t a problem.
If your scans show that you have brain cancer, the doctor will refer you to a cancer specialist called an oncologist. If there’s one in your area, you should see a specialist in brain tumors called a neuro-oncologist.
The next step is to confirm that you have cancer. Doctors usually do this by taking and testing a sample of the tumor. This is called a biopsy:
- They’ll find the exact location of the tumor with a CT or MRI scan.
- Most of the time the doctor will have to open your skull to get to the tumor. They’ll try to remove the whole tumor if they can. They’ll take a sample from the tumor for the biopsy.
- If they can’t get the entire tumor, they’ll remove a small piece.
- If they can get to the tumor without surgery, they’ll make a small hole in your skull and guide a needle through the hole to the tumor. They’ll collect the biopsy sample with the needle. This technique is called stereotaxis or stereotactic biopsy.
A doctor called a pathologist will examine the biopsy under a microscope. They specialize in diagnosing diseases by looking at cells and tissues.
Brain Cancer Scans
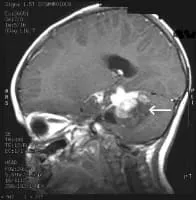
MRI Brain Cancer Picture: Side view section through the brain of a young girl. The white arrow shows a brain tumor that involves the brainstem.
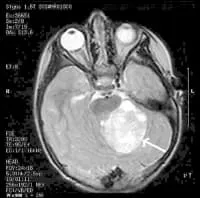
MRI Brain Cancer Picture: Cross-section (image taken from the top of the head down) of a brain tumor in a young girl. The white arrow shows the tumor.
Can You Travel If You Have Brain Cancer?
While brain cancer can limit where, when, and how you travel, getting away may be good for you. A trip -- whether for work, pleasure, or to go to a clinical trial -- may help you know that you can still do things that you want to do.
But before you book your trip, you’ll want to check on these things.
Driving. The doctor will let you know if it’s OK based on the location of your cancer and symptoms like vision trouble or seizures.
Flying. You should be able to fly about 3 months after you finish brain cancer treatment. But check with your doctor first. Changes in pressure could cause headaches or brain swelling.
Treatments. If the trip might make you miss a cancer treatment, talk to your doctor about rescheduling. And get a letter from your doctor explaining your condition and treatments, especially if you have a port or medical implant and plan to go through airport security. If you’re going somewhere that English isn’t widely spoken, make a copy of the letter in that language. You may also want to wear a special medical alert bracelet if you could have seizures.
Arrange medical care ahead of time. Make a list of resources in the area that you’ll visit. Include a doctor, hospital that treats brain cancer, and urgent care center. If you need lab work while you’re away, your doctor can help you figure out where and when to have this done.
During your trip
To stay well and curb stress levels while you travel:
Keep your medicine with you. Checked luggage can get lost. Pack prescription meds in your carry-on bag for flights. Keep them in their original packages, which show what they are. You may also want to bring extra in case your trip home gets delayed.
Avoid germs. Wash your hands or use hand sanitizer often.
Protect your skin. Use sunscreen. Many cancer treatments can make you more likely to get a sunburn.
Keep up your energy. Drink plenty of water during the day and carry snacks with you. Eating small meals often will help, too.
Pace yourself. Travel can be tiring for anyone. In a big airport or train station, it’s OK to ask for help getting to your gate or a wheelchair. At your destination, consider what’s realistic for you to do in a day, rest when you need to, and enjoy your trip.
