- Headaches Overview
- Migraine
- Cluster & Tension Headaches
- Other Types of Headaches
- View Full Guide
Lifestyle Strategies That Might Help Your Migraines

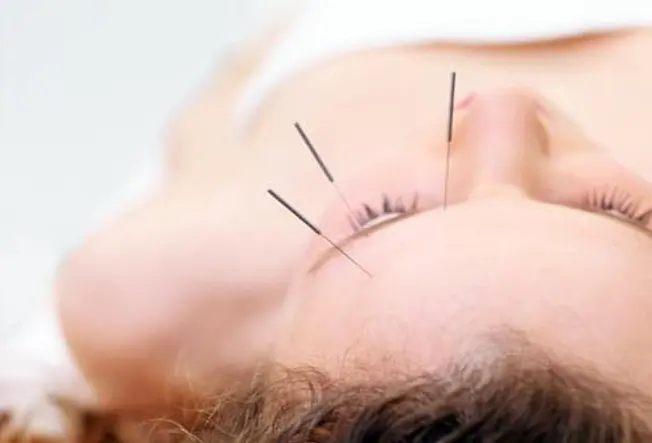
Acupuncture
In this traditional Chinese practice, an expert puts tiny needles into your body at specific points. Small studies suggest it can ease migraine pain and may also lower the number of headaches. You should still keep up with your other treatments, too.
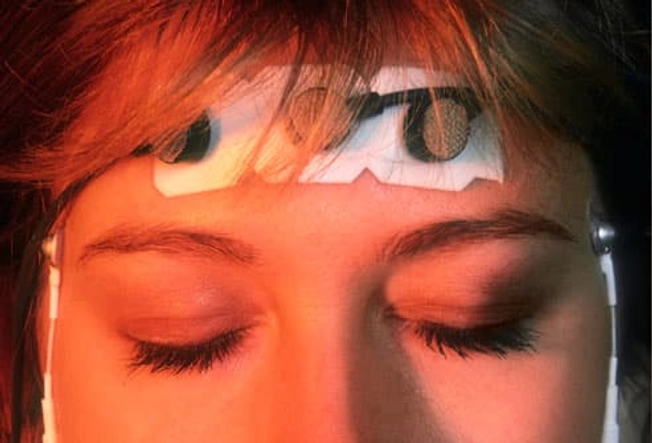
Biofeedback
Your body responds to pain with physical changes like a higher heart rate, tensed muscles, or cold hands. In biofeedback, sensors measure these shifts, then feed the information to you as a blinking light or a tone you can hear. You learn to respond to the feedback and relax your muscles. Some studies show it can often ease headache pain and how often you get migraines.
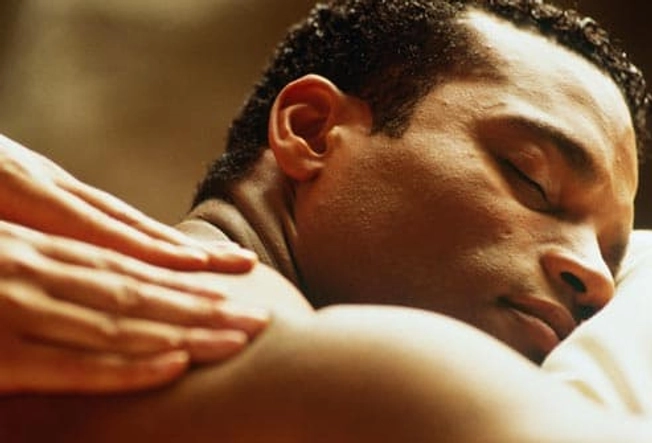

Massage
Early research shows massage may lower the number of headaches in some people. It doesn't help with pain once a migraine starts. Massage can also ease stress, a common headache trigger.
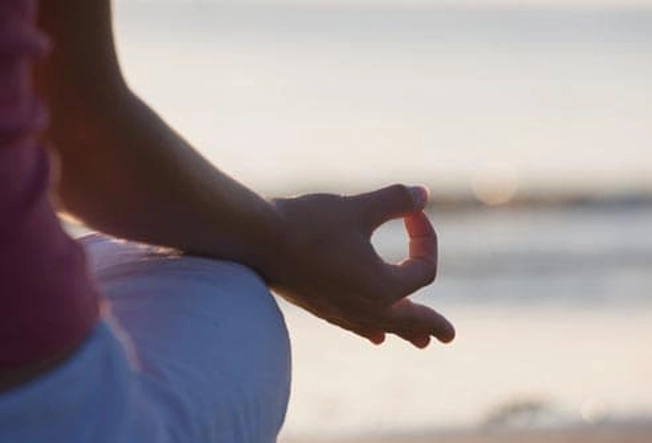

Relaxation Techniques
Because migraines are often triggered by stress, relaxation training is a great idea. Methods include deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, in which you tense and relax the muscles in different parts of your body. With practice, this technique can improve how you handle stress, which may cut down on headaches.
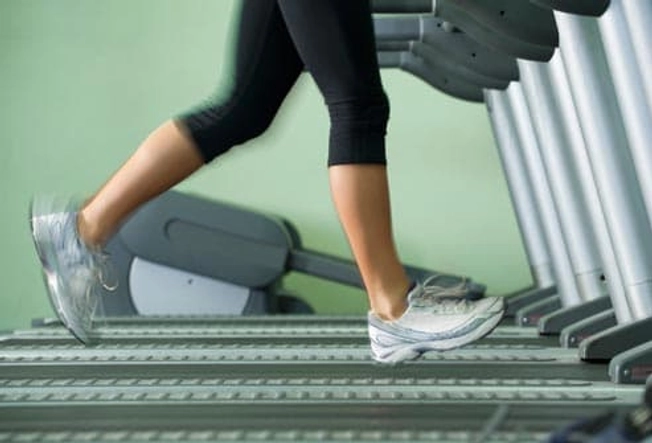

Exercise
Regular cardio exercise -- workouts that get your heart pumping -- could make a difference. A Swedish study compared exercise with relaxation and a drug that prevents migraines. The cardio routine -- 40 minutes, three times a week -- worked as well as relaxation or medicine in cutting down on pain and how often headaches strike.
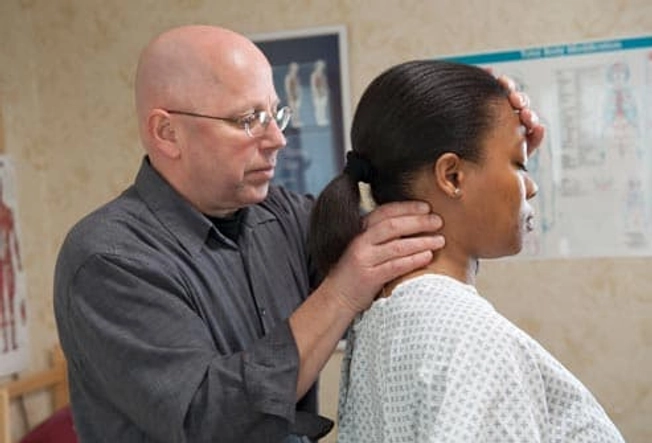
Spinal Manipulation
There's some question about whether this technique, also called getting "adjusted" by a chiropractor, can help with migraines. But one small study found it worked just as well as medication to prevent headaches.
There are some risks with this treatment, so talk to your doctor before trying it.
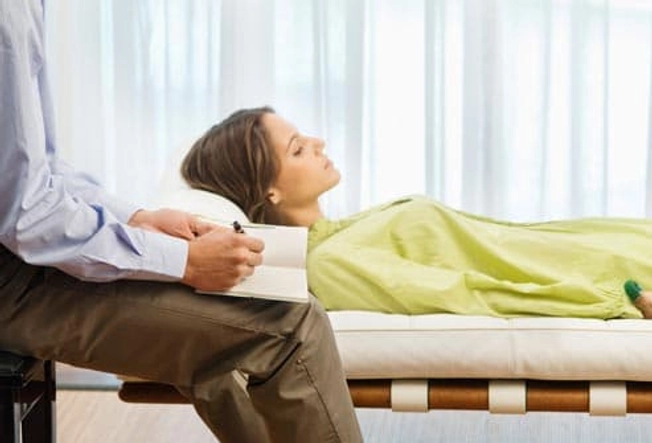

Talk Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy, which focuses on changing your thoughts and actions, may help you have fewer migraine symptoms.
Getting therapy doesn't mean you have emotional or mental problems. It can give you a fresh approach to situations that usually give you headaches. It works especially well when you also do other preventive treatments.

Diet Changes
Some people find that certain foods trigger their migraines. Some of the most common culprits are alcohol, caffeine, chocolate, canned foods, cured or processed meats, aged cheeses, cultured dairy (such as yogurt), MSG, and aspartame.
Write down your meals and snacks in a "food diary" to help you remember what you ate before a headache came on. Then cut out these foods one at a time to see if it helps.
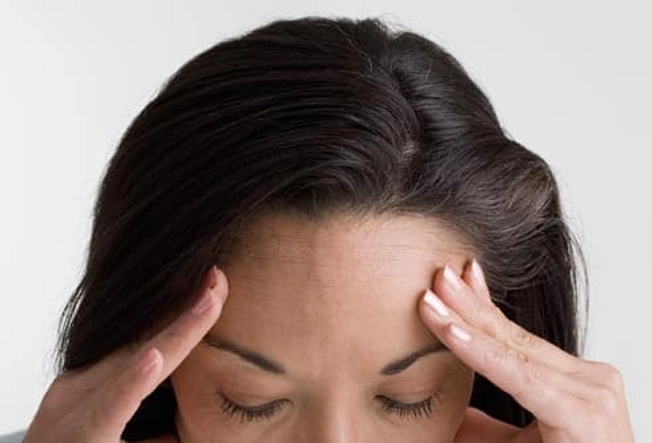

Pressure
Many people find that putting gentle pressure on the head, face, and neck during a migraine can help ease the pain. Techniques to try:
- Press your brow line and under your eyes.
- Rub your temples and jaw in a circular motion.
- Massage the base of your skull with a tennis ball.
A variety of head wraps and bands claim to ease migraine pain. They're inexpensive and might be worth a try.
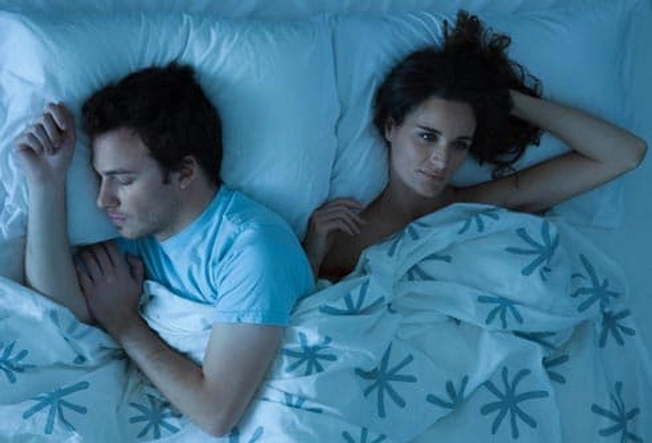

Sleep
Studies show that poor sleep and migraines often go hand in hand. So rethink your routine. Things to try to get better shut-eye:
- Don't read, watch TV, or listen to music in bed.
- Don't take naps.
- Don't eat heavy meals within a couple of hours of bedtime.
- Don't use your phone, laptop, or tablet at bedtime.
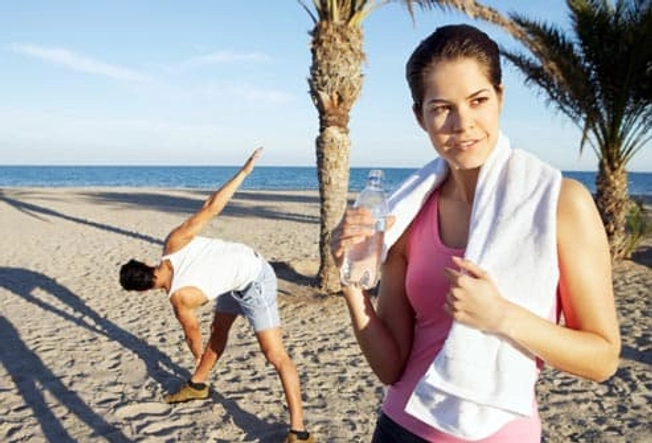

Keep Up Good Habits
Your lifestyle can have a big impact on how often you get your headaches. These tips can help:
- Don't skip meals.
- Stay hydrated.
- Get regular exercise.
- Stay at a healthy weight.

Why Try Treatments That Aren't Drugs?
They may be a good option if you:
- Don’t get relief from prescribed treatments
- Have trouble with medicine side effects
- Have a condition that keeps you from taking migraine drugs
- Simply don't want to take medication

Do Your Homework
If you’d like to try a new way to treat your migraine, your doctor can tell you how well it works and if there are any risks. They may know of an expert who specializes in these treatments. And they can check to make sure they won’t have bad side effects.