Common Adult Skin Problems Slideshow: Shingles, Hives, and More


Got Skin Problems?
Is your skin itchy, broken out, or covered in a rash or strange spots? Skin inflammation, changes in texture or color, and spots may result from infection, a chronic skin condition, or contact with an allergen or irritant. If you think you have one of these common adult skin problems, have your doctor check it out. Most are minor, but others can signal something more serious.
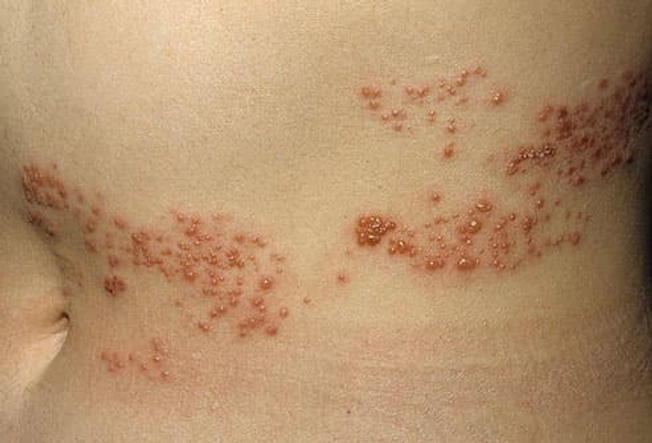
Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
A rash of raised dots that turns into painful blisters, shingles causes your skin to burn, itch, tingle, or become very sensitive. Shingles often shows up on your trunk and buttocks, but can appear anywhere. An outbreak lasts about two weeks. You’ll recover, but pain, numbness, and itching might linger for months, years, or even the rest of your life. Treatment includes creams for your skin, antiviral drugs, steroids, and even antidepressants. It’s important to be treated early to help prevent complications.
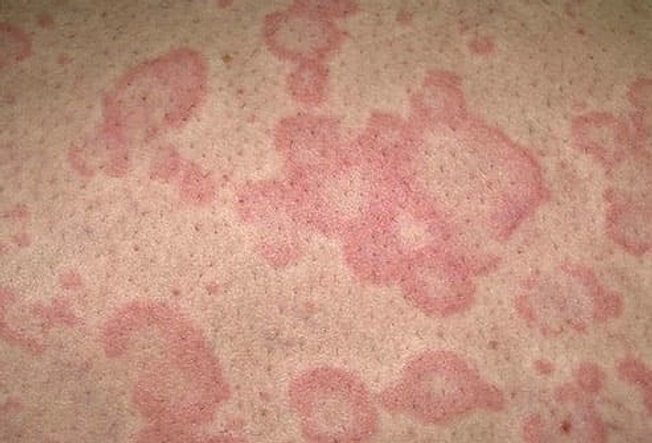
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives look like welts and can itch, sting or burn. They vary in size and sometimes join together. They may appear on any part of you and last anywhere from minutes to days. Causes include extreme temperatures, infections like strep throat, and allergies to medications, foods, and food additives. Antihistamines and skin creams can help.
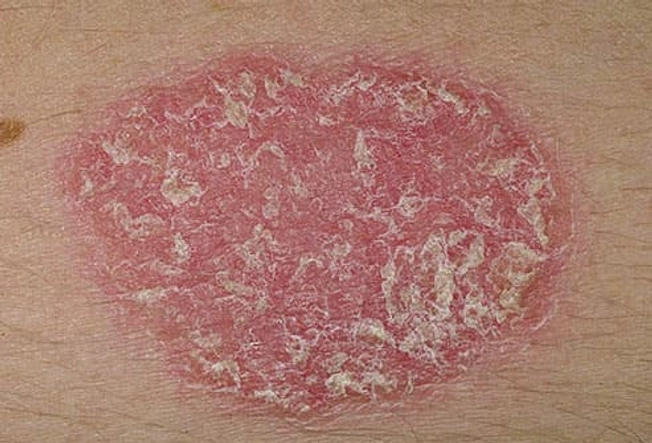
Psoriasis
Thick, red patches of skin covered with white or silvery scales are signs of psoriasis. Doctors know how psoriasis works -- your immune system triggers new skin cells to grow too quickly -- but they don't know what causes it. The patches typically show up on your scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. They can heal and come back throughout your life. Treatments include creams and ointments for your skin, light therapy, and medications taken by mouth, injection, or IV.
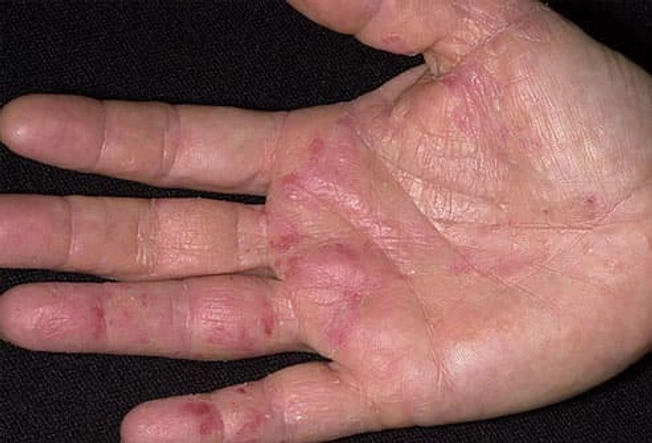
Eczema
Eczema is a blanket term for several non-contagious conditions that cause inflamed, red, dry, and itchy skin. Doctors aren't sure what makes eczema start in the first place, but they do know that stress, irritants (like soaps), allergens, and climate can trigger flares. In adults, it often appears on the elbows, hands, and in skin folds. Several medications treat eczema. Some are spread over the skin, and others are taken by mouth or as a shot.
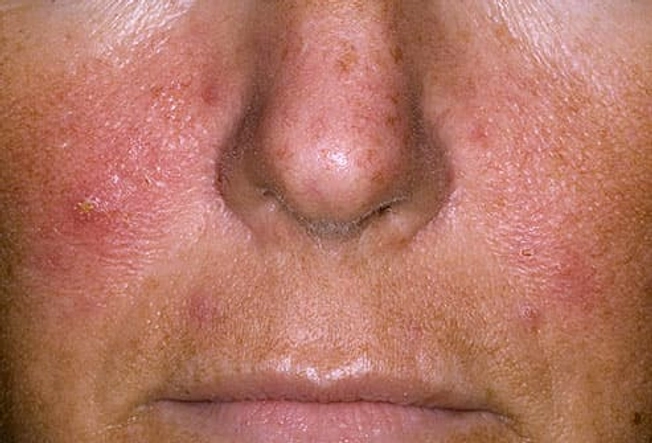
Rosacea
A tendency to flush easily, followed by redness on your nose, chin, cheeks, and forehead could be rosacea. It can get redder over time with blood vessels you can see. You may have thickened skin, bumps, and pus-filled pimples. It could even affect your eyes. Medications taken by mouth or spread on the skin are available. Doctors can treat broken blood vessels and red or thickened skin with lasers.
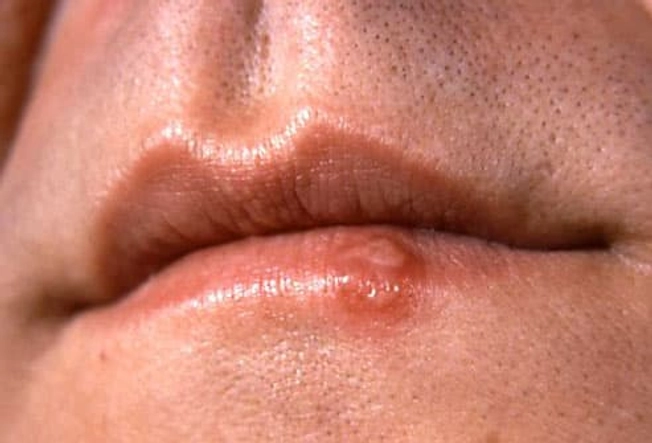
Cold Sores (Fever Blisters)
The herpes simplex virus causes small, painful, fluid-filled blisters on your mouth or nose. Cold sores last about 10 days and easily spread from person to person. Triggers include fever, too much sun, stress, and hormonal changes like periods. You can treat cold sores with antiviral pills or creams. Call your doctor if the sores contain pus, the redness spreads, you have a fever, or if your eyes become irritated. These can be treated with prescription pills or creams.
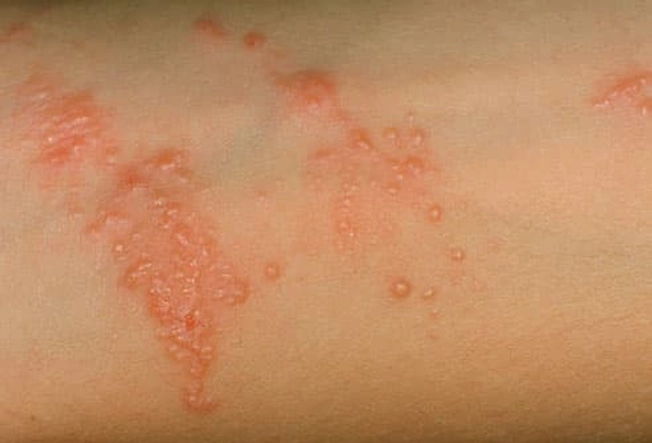
Rash From Plants
Contact with the oily coating from poison ivy, oak, or sumac causes a rash in many people. It begins with redness and swelling at the site, and then becomes itchy. Blisters usually show up within 12 to 72 hours after you touch the plant. A typical rash looks like a red line, the result of the plant dragging across your skin. An outbreak usually lasts up to 2 weeks. Treatment can include medicine spread on the skin or taken by mouth.
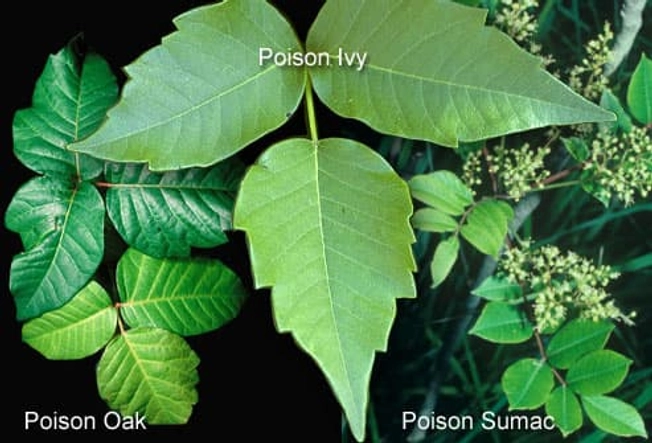

Soothe Itchy Plant Rashes
Prescription or over-the-counter medication can help soothe the itch. Try cool compresses and oatmeal baths, too. Your doctor may prescribe medication for a severe rash and antibiotics for an infection. Learn to spot these plants so you can avoid direct contact. In general, poison oak grows west of the Rockies; poison ivy to the east.
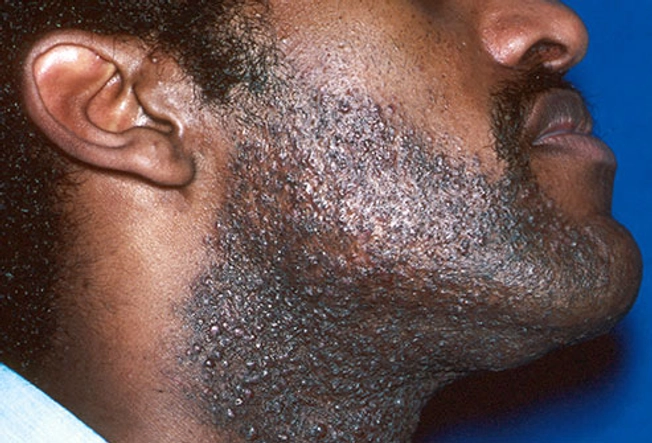
Razor Bumps
Pseudofolliculitis barbae occurs when hair follicles become inflamed because of shaving. It most often occurs on the face and neck but can happen anywhere that you shave or pluck. Also known as “razor bumps” or “shaving bumps,” the irritation can cause pimples, and even scars. You can minimize the problem with by taking a hot shower or applying a hot towel before you shave. Use shaving cream or foam and pull the blade in the direction your hair grows. Rinse with cold water and apply moisturizer.
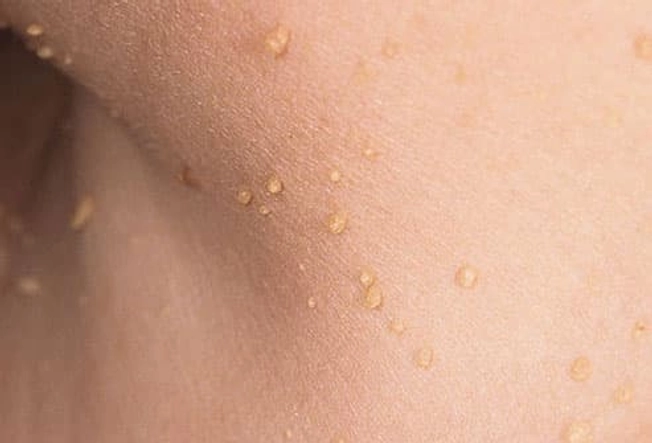
Skin Tags
This small flap of flesh-colored or slightly darker tissue hangs off your skin by a stalk. They're usually found on the neck, chest, back, armpits, under the breasts, or in the groin area. Skin tags appear most often on women and elderly people. They aren’t dangerous and usually don't cause pain unless they become irritated when clothing or nearby skin rubs against them. A doctor can cut, freeze, or burn them off.
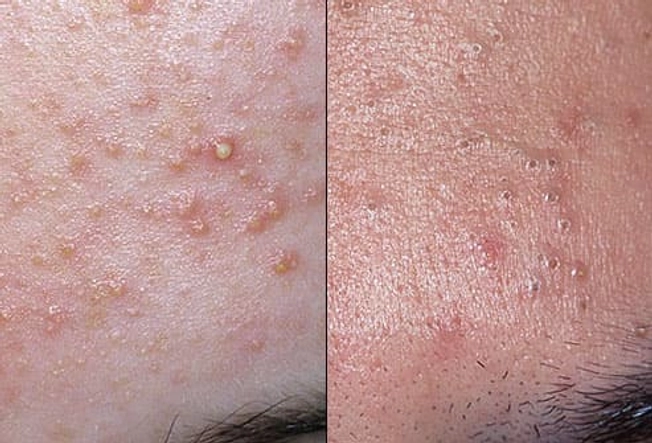
Acne
Acne breaks out when a pore clogged with oil and dead skin cells gets inflamed. Pores that stay open and turn dark are called blackheads; completely blocked pores are known as whiteheads. Bacteria and hormones trigger acne, which most often shows up on your face, chest, and back. You can also get pus-filled pimples and cysts. To help control acne, keep oily areas clean and don't squeeze (this may cause infection and scars).
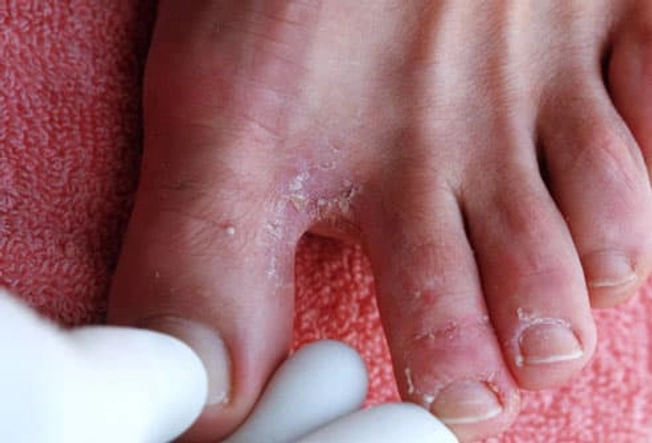
Athlete's Foot
This fungal skin infection causes your feet to peel, turn red, itch, and burn. You may also get blisters and sores. Athlete's foot is contagious and passed through direct contact. To prevent it, don't share shoes with an infected person or walk barefoot in areas like locker rooms or near pools. Treat it with topical antifungal lotions. A doctor can prescribe medications for more severe cases. During treatment, you’ll need to keep your feet and the insides of your shoes clean and dry.
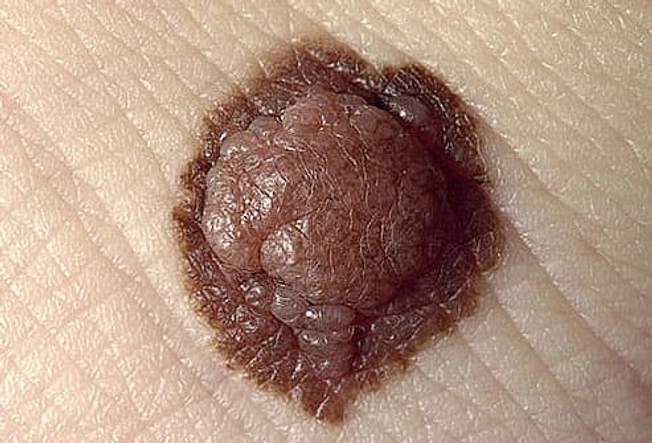
Moles
Moles, which are usually brown or black, can be anywhere on the body. They might show up alone or in groups and generally appear before age 20. Some moles change slowly over the years. They can go from flat to raised, grow hair, or change color. Get your moles checked once a year by a dermatologist. See your doctor right away for any that change, have irregular borders, are an unusual or uneven color, bleed, or itch.
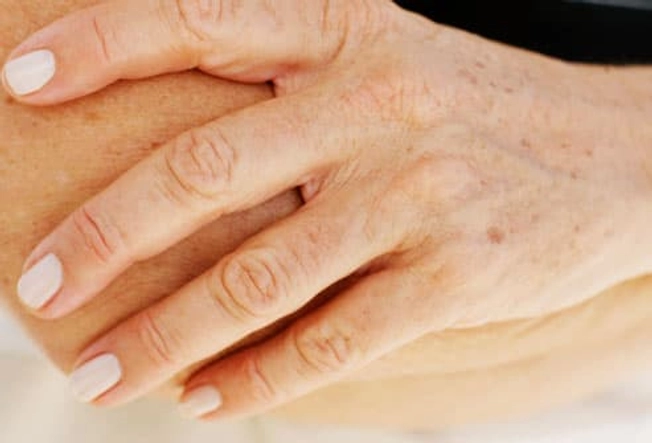
Age or Liver Spots
These pesky brown or gray spots aren’t really caused by aging, though they do become more common as you get older. You get them from exposure to sunlight, which is why they tend to appear on your face, hands, and arms. You can try bleach creams, acid peels, and light-based treatments to fade them. See a dermatologist to rule out serious problems like melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
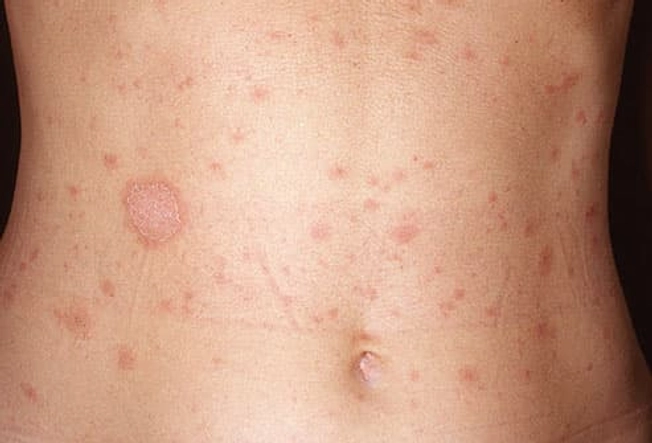
Pityriasis Rosea
A harmless rash, pityriasis rosea usually begins as a single scaly, pink patch with a raised border. Days to weeks later, it starts to itch and spread. The rash may be in the shape of a Christmas tree spread across your body. Doctors don't know for sure what causes it, but they don't think it's contagious. It often goes away in 6 to 8 weeks without treatment. Pityriasis rosea most often shows up between the ages of 10 and 35.
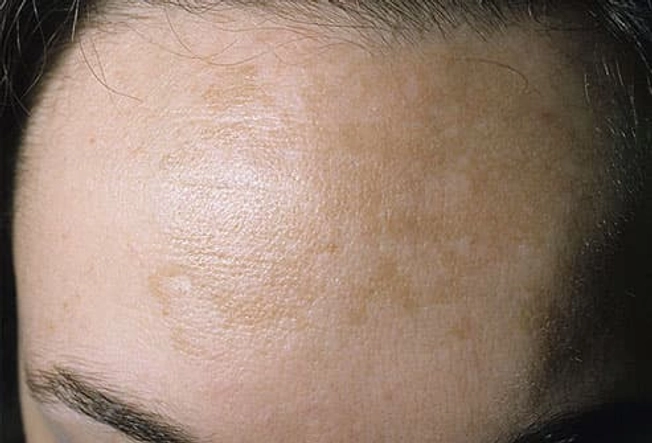
Melasma ('Pregnancy Mask')
Melasma (chloasma) is tan or brown patches on your cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. It’s often called the "pregnancy mask" because it happens in half of all pregnant women. Men can get it, too. If it doesn’t go away on its own after the baby comes, you can treat it with prescription creams, over-the-counter products, or with laser treatments. Sunlight makes it worse, so always use a broad-spectrum SPF 30 sunscreen.
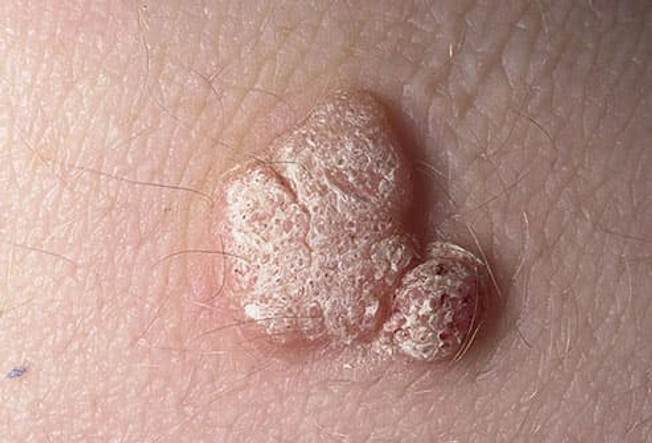
Warts
In most cases, common warts appear on the fingers or hands. They're caused by the human papillomavirus. Warts spread when you touch something used by a person with the virus. To prevent more warts, cover them with bandages, keep them dry, and don’t pick them. They're usually harmless and painless. You can treat them with topical medications, or a doctor can freeze or burn them off. More advanced removal techniques include surgery, lasers, and chemicals.
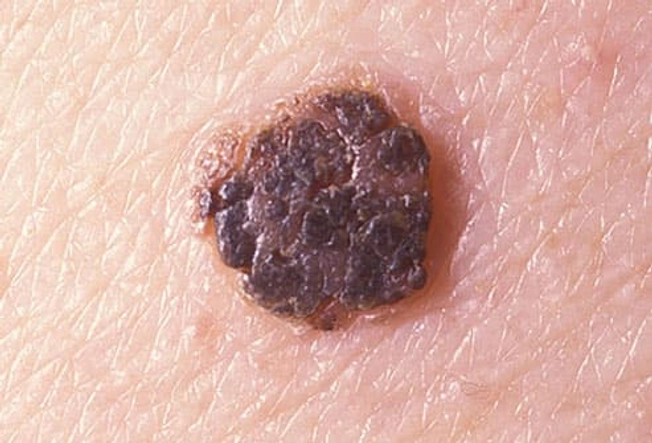
Seborrheic Keratoses
Seborrheic keratoses are noncancerous growths that often show up as you age. They can appear on many areas of the skin either alone or in groups. They may be dark or multicolored, and they usually have a grainy surface, though they can be smooth and waxy. You don't need to treat them unless they get irritated or you don’t like the way they look. They're easy to mistake for moles or skin cancer, but a dermatologist can tell the difference.