How Meningitis Spreads
Hide Video Transcript
Video Transcript
SPEAKER
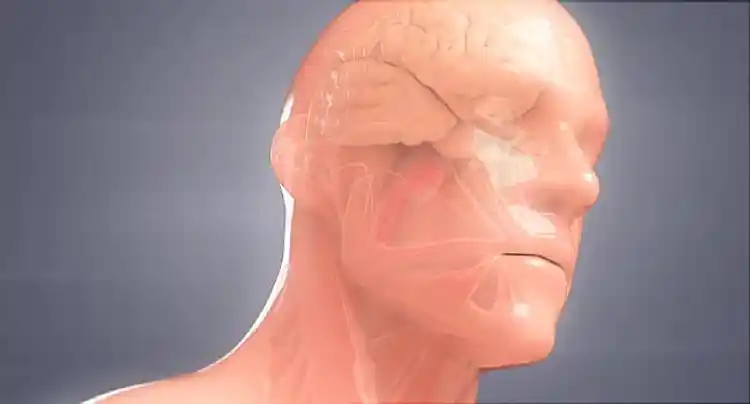
The brain, the command center to your entire nervous system. And yet the tiniest of germs can bring this complex organ to a halt. Meningitis is caused by germs that can do just that-- an infection that attacks the lining around the brain and spinal cord. If not treated early, this culprit can be dangerous.
Infectious meningitis can take many forms-- viral, fungal, and bacterial, which can be the deadliest. But how does it make its attack on your brain?
When bacteria gets near your face or in your mouth, they can break through the protective lining of your nose and throat. At this point, they can multiply at an alarming rate, infecting the bloodstream. The infection can spread to the meninges, a protective layer of tissue that pads your brain and spinal cord. This layer expands when fighting the infection.
However, while it is protecting your brain, your body can suffer. The impact of the swelling will be seen in a number of ways.
The inflammation produces a fever or headache. It can also interfere with memory and concentration. You may experience sensitivity to light. Muscles can ache, possibly a stiff neck. Bleeding under the skin can look like a rash.
Things become most serious when the bacteria crosses the blood-brain barrier. This could mean more inflammation and swelling around the brain.
The increased pressure can cause weakness of the muscles in the face. Blood clots can form, which can lead to stroke.
Meningitis onset can be rapid, so being just as quick to understand your body's warning signs could prevent germs from doing long-term damage.
[MUSIC PLAYING]