What You Should Know About Opioids

What Are They?
Also called narcotics, opioids are a kind of pain medication your doctor may give you after an accident or surgery, or as treatment for a chronic disease like arthritis. Most are made from the opium plant, but some (called synthetic opioids) are made in a lab. Either way, they affect the reward center of your brain and boost your levels of certain brain chemicals that block pain, slow your breathing, and generally make you feel calm.
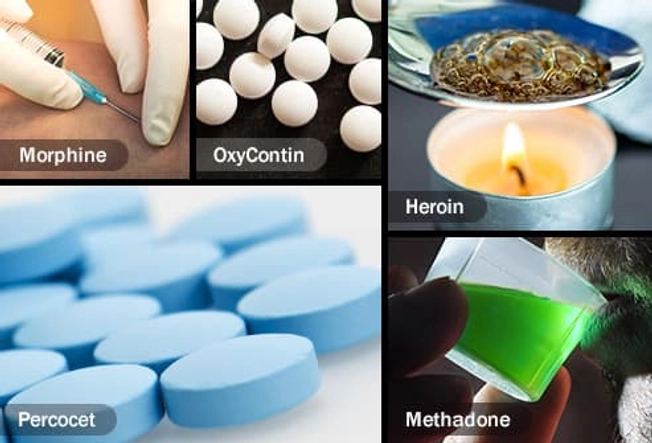
Types
Opioids have different strengths, and some are legal and some aren’t. Examples include:
- Codeine
- Meperidine (Demerol)
- Oxycodone (OxyContin)
- Oxycodone and acetaminophen (Percocet)
- Fentanyl
- Hydrocodone and acetaminophen (Lortab, Norco, Vicodin)
- Methadone
- Morphine
- Heroin

Short-Acting vs. Long-Acting
Short-acting opioids, like Vicodin or Percocet, get medication into your system quickly. When you take them as directed, like immediately after surgery, you probably won’t have any issues. But if you take them for too long, it may be hard to stop. Long-acting opioids, like OxyContin, give your body a smaller amount of medication over a longer time. They’re used to treat diseases that cause chronic pain, like fibromyalgia or arthritis.

How to Use Opioids
If your doctor prescribes them for you, be sure to follow the directions. It’s usually best to take them on a regular schedule. If you wait until the pain is bad, you might need more medication, which makes you more likely to have side effects.

Common Side Effects
All medications have side effects, and opioids are no different. The most common one with short-term use is constipation. Others include:
- Depression
- Hot flashes
- Erectile dysfunction
- Weight gain
- Weak immune system

Dependence
The longer you take opioids, the greater the chances that your body will get dependent on them. If that happens, you may have withdrawal symptoms -- like anxiety, a fast heart rate, sweating, nausea, and chills -- when you stop taking them. This is more likely if you try to stop too quickly instead of tapering off slowly. Talk to your doctor about how to stop safely.

Dependence vs. Addiction
If you've become addicted to an opioid, you'll have strong cravings for them that will be hard to resist. Other signs can include:
- Using more than your doctor prescribed
- Feeling powerless to stop the cravings
- Acting irresponsibly, possibly in an effort to get more drugs
- Mood swings, irritability, and feeling agitated
A Growing Problem
While most people use these medications safely, up to 12% of people who take them for chronic pain become dependent on or addicted to them. From there, some people move on to street drugs. About 80% of people who use the illegal opioid heroin say they misused a prescription one first. Heroin is often cheaper and easier to get.

What Raises Your Chances of Addiction?
Anyone can become addicted to opioids, especially if they don’t follow their doctors’ instructions. But some people may be more likely to than others. This includes people who:
- Have had addiction issues with alcohol, tobacco, or other substances
- Have a family history of substance abuse
- Are in their teens or early 20s
- Are female. (Women report chronic pain more often, and they may also become dependent more quickly than men.)

Treatment for Addiction
If you've become addicted, you may need a specialized program that could include medication to ease withdrawal symptoms, counseling to deal with cravings and depression, and guidance to help you avoid a relapse. For help with an opioid addiction, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).

What to Do in Case of Overdose
This can be life-threatening. If you think someone might have overdosed, call 911 right away. Warning signs include:
- Loss of consciousness or being very sleepy
- Slow or irregular breathing
- A slow pulse
- Vomiting
- Small pupils
If you or a loved one is dealing with opioid addiction, ask your doctor about a prescription nasal spray called naloxone (Narcan) that can quickly reverse the effects of an overdose. You may be able to keep it on hand in case of an emergency.
Other Options for Pain Relief
Ask your doctor if a strong nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), like diclofenac (Cataflam) or prescription-strength ibuprofen, might work for moderate pain. For chronic pain, you might try nondrug treatments like massage, exercise, or acupuncture, along with non-opioid medication.