Medication Side Effects You Shouldn’t Ignore
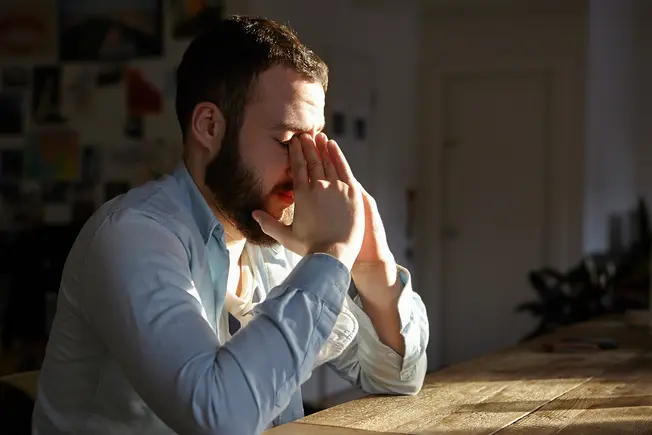


Anxiety
Substance-induced anxiety is anxiety caused by taking certain medications – sometimes even medications meant to treat anxiety itself. Anxiety can rob you of sleep, affect concentration, cause chest pain, and make it hard to eat.

Digestive Woes
Some digestive side effects can make it hard to get the right nutrition or can deplete your body of fluids and nutrients. Pay attention to GI problems such as diarrhea, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, and lack of appetite.

Dizziness
Feeling dizzy isn’t life-threatening, but it can raise your risk of falls that cause injury to your body.
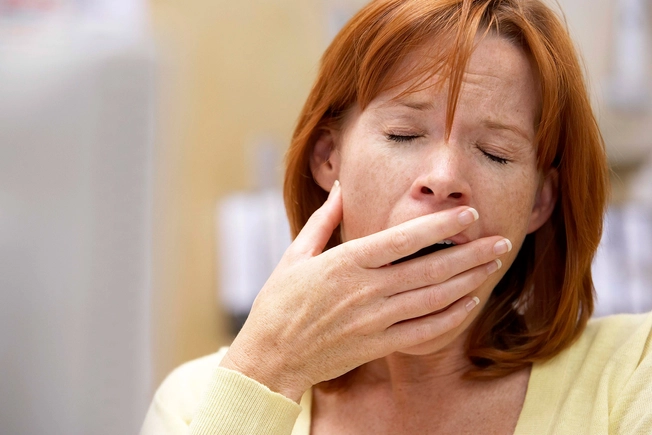

Drowsiness
Another cause of falls is feeling sleepy. Drowsiness from medication can make driving dangerous, affect your work performance, and make it hard to do daily tasks.
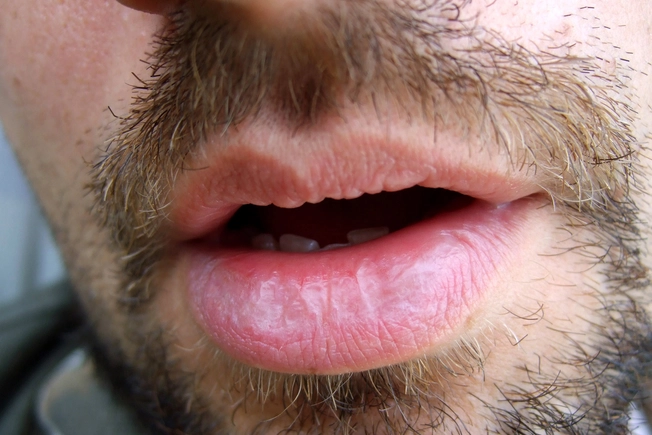
Dry Mouth
Saliva is important for oral health, and when a medication dries your mouth out, you raise your chances of getting plaque, tooth decay, and gum disease. You may also deal with mouth sores, yeast infections in the mouth (thrush), and cracked lips.

Hallucinations
Some medications may cause you to see things that aren't there, and the chance of this happening is even higher if you take multiple medicines. These visions can be scary and make you act in a dangerous way that harms you or others.
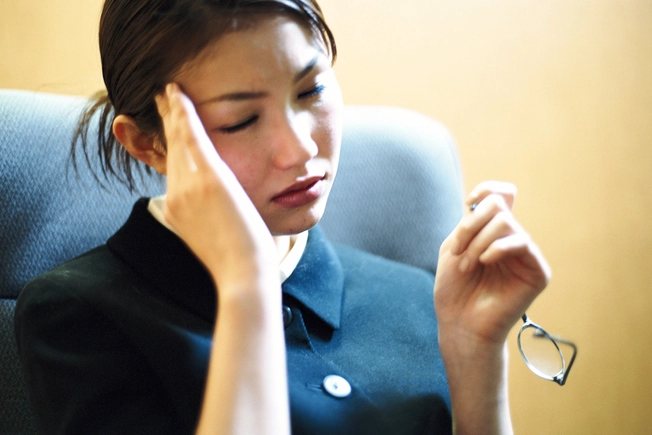

Headache
It’s common to deal with head pain when taking medications, but headaches are worth watching. Medication overuse or rebound headaches can happen when you take headache medicine for long periods of time.
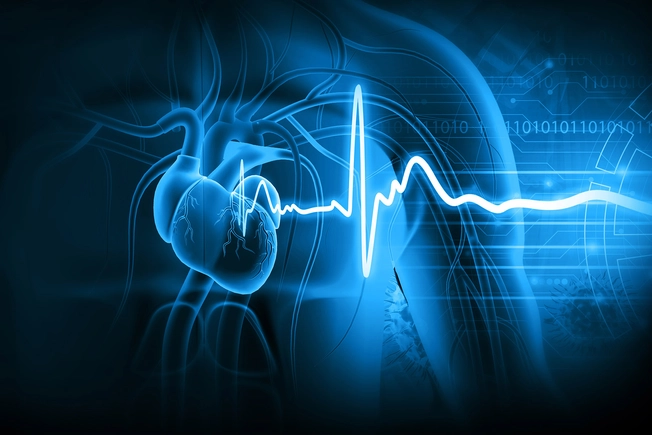
Heart Problems
Some medications cause faster or skipping heartbeats (heart palpitations). You may also have chest pain. Get chest pain checked out right away because it can have several causes, both heart-related and not. Pill-induced esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus) is a rare cause of acute chest pain.
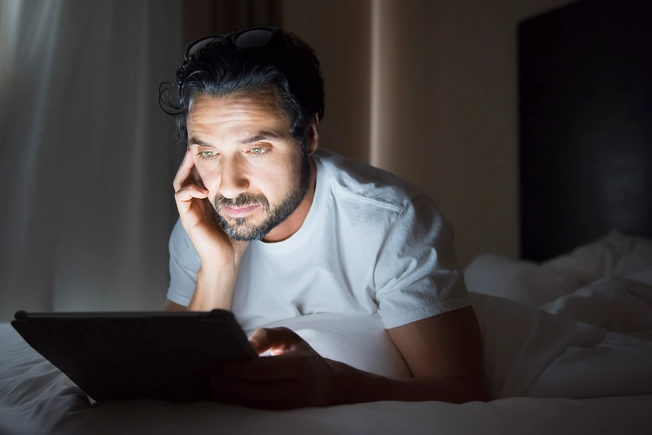

Insomnia
When your medications make it hard to sleep, over time your physical and mental health can decline. Your risk goes up for diabetes, high blood pressure, mood disorders, weight gain, driving accidents, injuries, and falls.
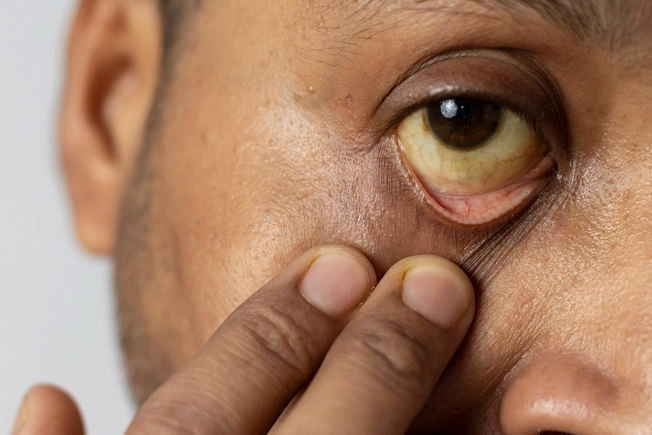
Jaundice
Though it’s rare, too much of certain medications can cause hepatitis, or inflammation of your liver. In addition to yellowed skin (jaundice), you may notice belly pain, tiredness, and GI problems, and you might have a fever. Untreated hepatitis can damage your liver and may even need a liver transplant in rare cases.
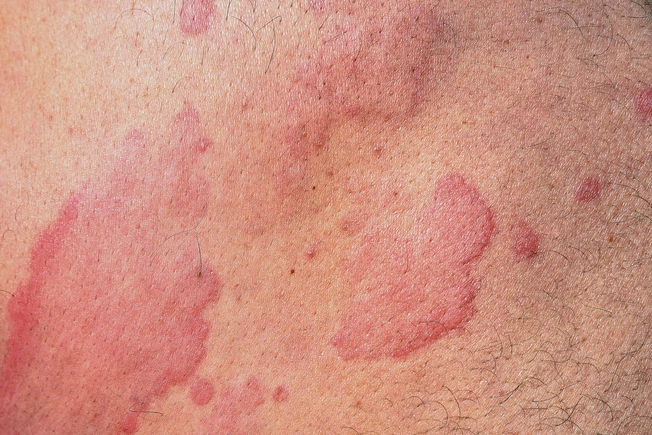
Rash
About 5% to 10% of severe drug reactions are allergic reactions. Most commonly, this shows up as a rash, or hives, on your skin. Serious allergic reactions can make it hard to breathe and be life-threatening. Blisters on your lips, mouth, eyes, and genitals may be a sign of a serious drug reaction called Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
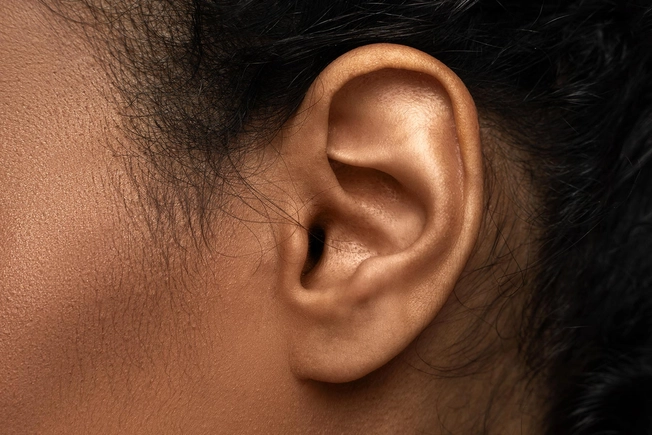
Ringing Ears
Tinnitus is a condition that causes ringing, buzzing, roaring, clicking, hissing, or humming in your ears. It can have a negative impact on your life, making it hard to concentrate, affecting your mood, and preventing good sleep.
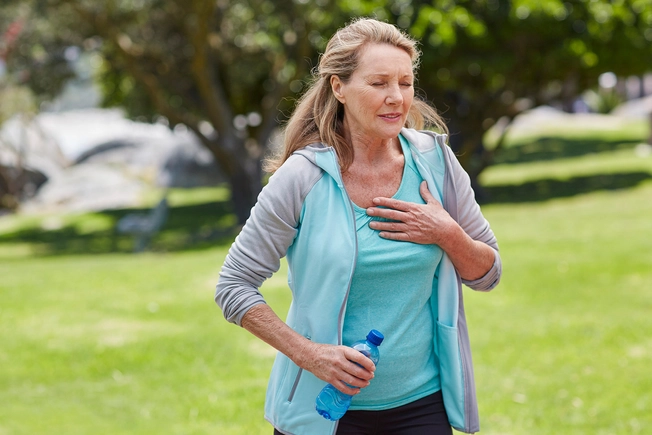

Shortness of Breath
Bad reactions to medications can sometimes cause lung diseases such as asthma, bleeding in your air sacs, autoimmune diseases that attack lung cells, and fluid buildup in the lungs. Get medical help right away if you’re wheezing, feeling chest pain from breath struggles, or coughing as you try to breathe.
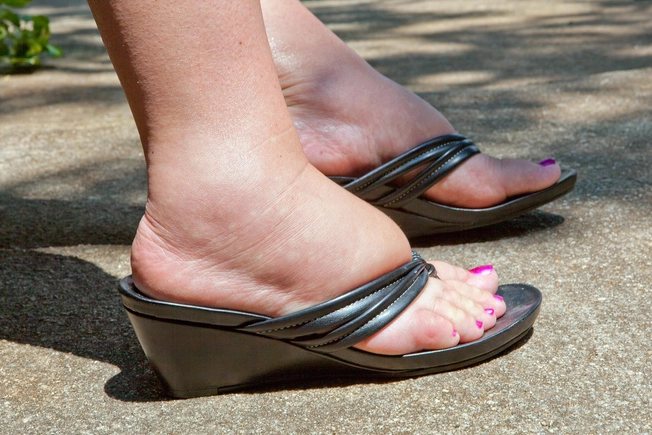

Swelling/Weight Gain
If your medication makes your body hold on to fluid, you may notice you have swollen arms and legs. Swelling that comes with shortness of breath, trouble breathing, or chest pain could be a sign of fluid collection in your lungs.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
- Aleli Dezmen / Getty Images
- Ratana21 / Getty Images
- Jupiterimages / Getty Images
- BananaStock / Getty Images
- tioloco / Getty Images
- urbazon / Getty Images
- Hitoshi Nishimura / Getty Images
- Rasi Bhadramani / Getty Images
- Jacobs Stock Photography Ltd / Getty Images
- Soumen Hazra / Getty Images
- anand purohit / Getty Images
- Jun / Getty Images
- Science Photo Library / Getty Images
- WebMD
SOURCES:
Tufts Medical Center: “Substance-Induced Anxiety Disorder.”
Johns Hopkins Medicine: “Medicines and the Digestive System,” “Drug-Induced Hepatitis.”
Cleveland Clinic: “Dizziness,” “Insomnia.”
Harvard Medical School: “What to do when medication makes you sleepy.”
Mayo Clinic: “Dry Mouth,” “Medication overuse headaches,” “Tinnitus.”
American Academy of Ophthalmology: “Medication-Related Visual Hallucinations: What You Need to Know.”
StatPearls: “Drug Induced Esophagitis.”
American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology: “Medications and Drug Allergic Reactions.”
PennMedicine: “Drug-Induced Pulmonary Disease.”