Uses
Methenamine is used to prevent or control returning urinary tract infections caused by certain bacteria. It is not used to treat an active infection. Antibiotics must be used first to treat and cure the infection. Methenamine is a drug that stops the growth of bacteria in urine. This medication also contains an ingredient that helps to make the urine acidic. When the urine is acidic, methenamine turns into formaldehyde to kill the bacteria.This drug is effective only against bacterial infections in the urinary tract. It will not work for other types of bacterial infections (such as in the blood) or for viral infections (such as the common cold or flu). Unnecessary use or misuse of any antibacterial drug can lead to its decreased effectiveness.
How to use Methenamine Hippurate
Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor. Dosage is based on the brand of methenamine you are prescribed, your medical condition, and your response to treatment. For children, dosage is also based on age and weight.
Methenamine works better if your urine is more acidic. Your doctor may test the acidity of your urine (urine pH). If necessary, your doctor may recommend ways to increase urine acidity (such as by taking vitamin C/drinking cranberry juice, limiting foods that decrease acidity/increase alkalinity such as milk products/most fruits, adjusting alkalinizing medications). See also Drug Interactions section. Follow your doctor's instructions.
For the best effect, take this drug at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time(s) every day.
Tell your doctor if symptoms of a urinary tract infection return (such as burning/painful/frequent urination).
Side Effects
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and loss of appetite may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Painful or difficult urination may occur with methenamine, although less often. Report these side effects to your doctor, who may need to lower your dose of methenamine or change your treatment to make your urine less acidic.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
Taking higher than recommended doses of methenamine may cause bladder irritation, painful/frequent urination, and bloody/pink urine. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms.
Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: mouth sores, unusual headache, ringing in the ears, muscle cramps, swelling of the arms/legs.
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US -
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
Before taking methenamine, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to formaldehyde; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: kidney problems, liver problems, dehydration.
Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).
During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
This drug passes into breast milk and the effect on a nursing infant is unknown. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
Interactions
See also How to Use section.
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.
Some products that may interact with this drug include: sulfonamide drugs (including sulfa antibiotics such as sulfamethizole), products that decrease the amount of acid in the urine (urinary alkalinizers such as antacids, sodium bicarbonate, potassium or sodium citrate, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as acetazolamide).
This medication may interfere with certain lab tests, possibly causing false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
Overdose
If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669.
Do not share this medication with others.
Lab and/or medical tests (such as urine tests, liver function) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later for another infection unless your doctor tells you to.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.
Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Images

methenamine hippurate 1 gram tablet
Color: whiteShape: oblongImprint: H 1This medicine is a white, oblong, scored, tablet imprinted with "H 1".
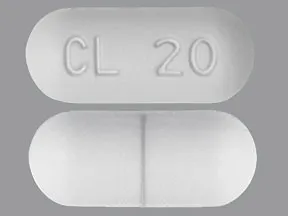
methenamine hippurate 1 gram tablet
Color: whiteShape: oblongImprint: CL 20This medicine is a white, oblong, scored, tablet imprinted with "H 1".

methenamine hippurate 1 gram tablet
Color: whiteShape: oblongImprint: E 71This medicine is a white, oblong, scored, tablet imprinted with "H 1".
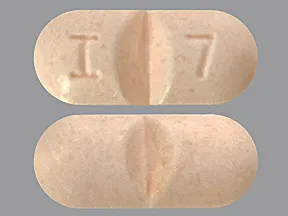
methenamine hippurate 1 gram tablet
Color: peachShape: oblongImprint: I 7This medicine is a white, oblong, scored, tablet imprinted with "H 1".
Are you currently using Methenamine Hippurate?
This survey is being conducted by the WebMD marketing sciences department.
Selected from data included with permission and copyrighted by First Databank, Inc. This copyrighted material has been downloaded from a licensed data provider and is not for distribution, except as may be authorized by the applicable terms of use.
CONDITIONS OF USE: The information in this database is intended to supplement, not substitute for, the expertise and judgment of healthcare professionals. The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that use of a particular drug is safe, appropriate or effective for you or anyone else. A healthcare professional should be consulted before taking any drug, changing any diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment.