Slideshow: A Visual Guide to Boils

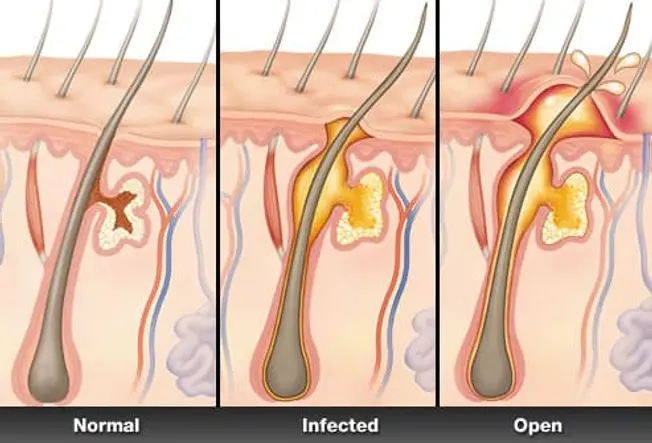
What Is a Boil?
A boil is a common, painful infection of a hair follicle and the surrounding skin. It begins as a red lump, then fills with pus as white blood cells rush in to fight the infection. Good home care can often clear up a single boil, also known as a skin abscess. A doctor's care is needed when a boil resists treatment or develops in certain vulnerable areas of the body.
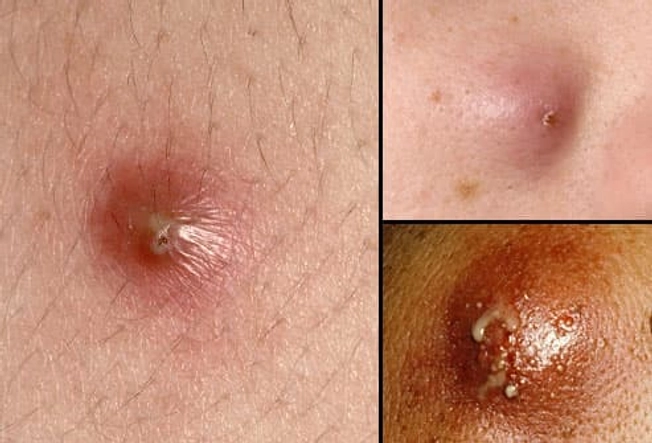
Boil Symptoms
Boils are usually pea-sized, but can grow as large as a golf ball. Symptoms can include:
- Swelling, redness, and pain
- A white or yellow center or tip
- Weeping, oozing, or crusting
You may also have a general feeling of ill health, fatigue, or a fever, which is reason to call a doctor.
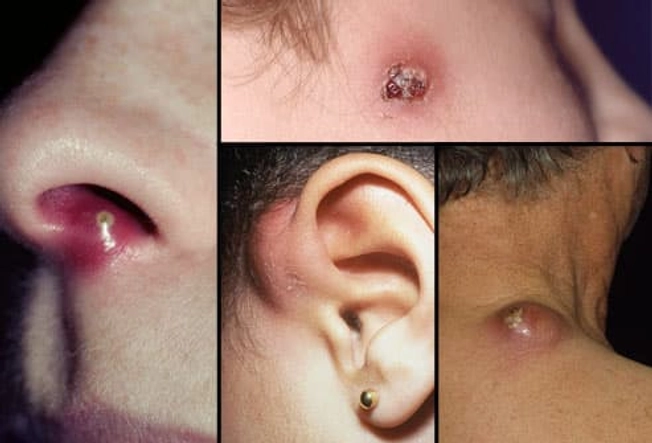
Where Do Boils Form?
Boils can form anywhere on the body, but they're most common on the face, neck, armpits, shoulders, back, and buttocks. Hairy, sweaty areas are typical sites, as well as areas of friction, such as the inner thighs. Boils can also develop around the ear or near the nose. The pain often worsens as pus collects under the skin, then eases as fluids begin to drain.
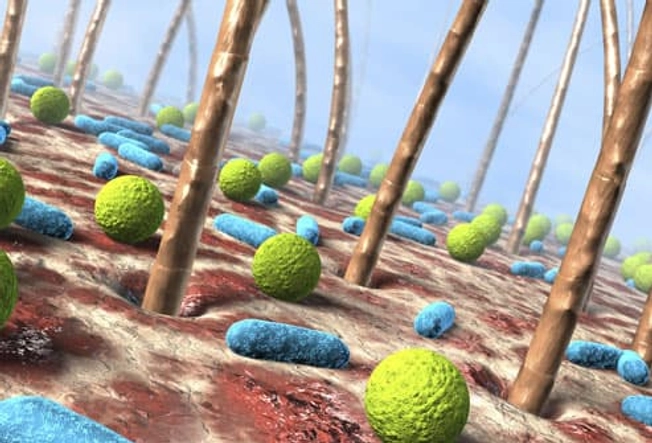
What Causes Boils?
Most boils are caused by staph bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus), which many healthy people carry on their skin or in their noses without a problem. When a scrape, cut, or splinter breaks the skin, the bacteria can enter a hair follicle and start an infection. Others boils, such as those associated with acne, develop from clogged pores that become infected.
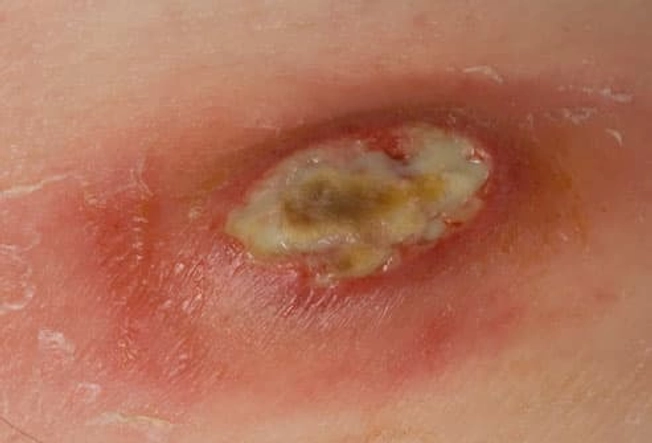
Ordinary Boil or MRSA Infection?
MRSA can look exactly like an ordinary boil: red, swollen, pus-filled, and tender. But MRSA infections are caused by one particular type of staph that is resistant to many antibiotics. If a skin infection spreads or doesn't improve after 2-3 days of antibiotics, your doctor may suspect MRSA. The right treatment given promptly is important to heal a MRSA infection and prevent a deeper, more dangerous infection.
Are Boils Contagious?
Not exactly, but the germs that cause boils (staph) are easily spread through skin-to-skin contact and contaminated objects. These bacteria usually do no harm unless they find a break in the skin. To avoid spreading staph, don't share towels, bedding, clothes, or sports gear while you have a boil. Avoid touching the boil, and keep it covered. Frequent hand washing can also help prevent spreading the bacteria.
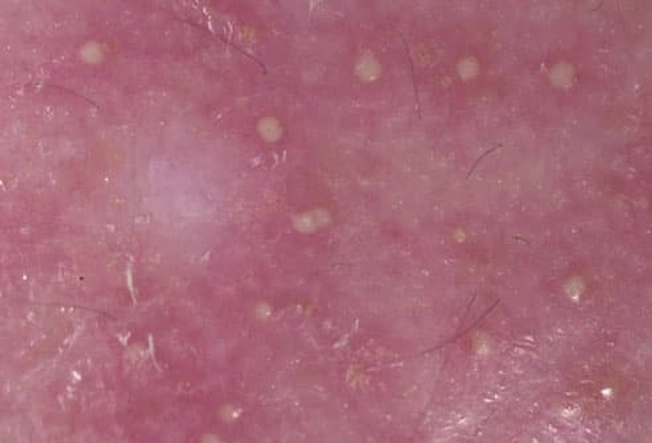
Early Warning: Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of the hair follicles that can develop into a boil. Tiny pimples with whiteheads appear around individual hairs, sometimes surrounded by red skin. It can be itchy, tender, and uncomfortable, but is typically not as painful or deep as a boil. Shaving or friction from tight clothing can let staph bacteria slip under the skin -- the most common cause of both folliculitis and boils.
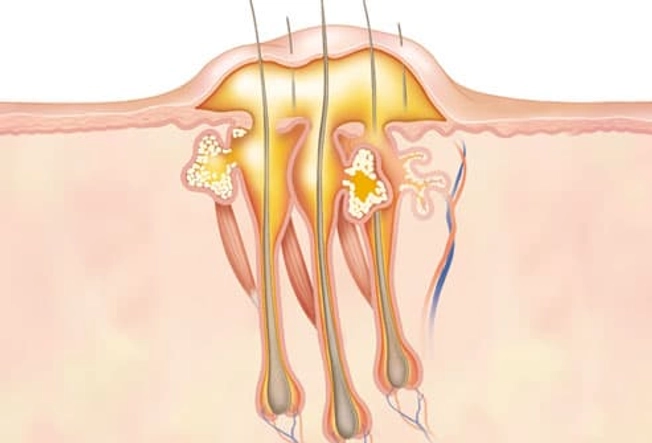
Boil Type: Carbuncle
When several boils form close together and join beneath the skin, it's called a carbuncle. They are most commonly found on the back and the neck but can develop anywhere. Men are more likely to develop carbuncles than women. A carbuncle tends to lie deeper beneath the skin than a boil and can take longer to heal.
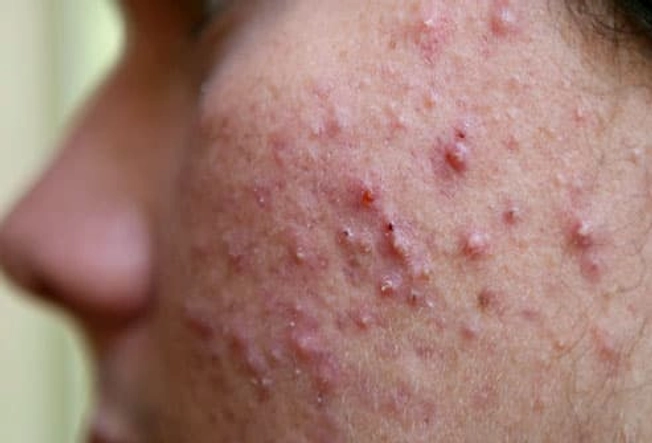
Boil Type: Cystic Acne
Cystic acne is a type of skin abscess that forms when oil and dead skin cells clog a hair follicle, creating a place where bacteria grow and thrive. It affects deeper skin tissue than regular acne, leading to firm, painful cysts. It's most commonly on the face and shoulders and typically occurs in the teenage years.
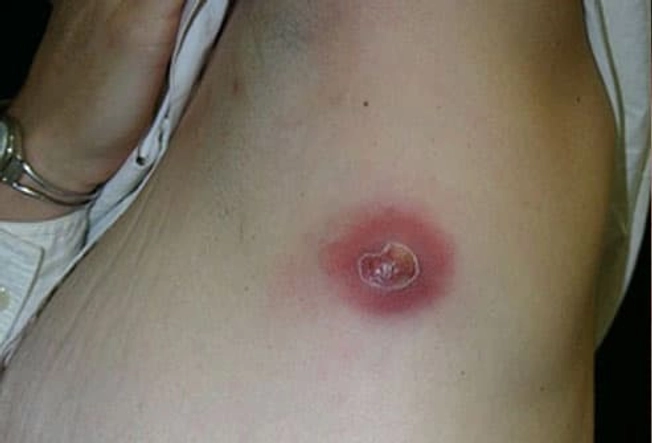
Boil Type: Armpit and Groin
When lumps and pus-filled abscesses repeatedly develop in these areas of the body, it may be a chronic condition called hidradenitis suppurativa. Infection starts in sweat glands and hair follicles that become blocked. Mild cases heal with home care. Several drugs and treatments are available for more serious and recurring cases.
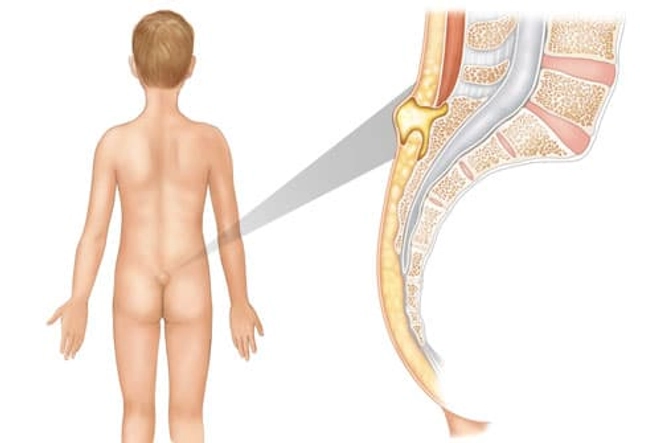
Boil Type: Pilonidal Abscess
When a boil forms in the skin just above the buttocks crease, it may be a pilonidal abscess. Hair is believed to play a role, and irritation, pressure, and prolonged sitting may also contribute to the development of a cyst here. If a cyst becomes inflamed and infected, it becomes an abscess. Some children are born with a "pilonidal dimple" where infections can crop up. Signs of infection require a doctor's attention.
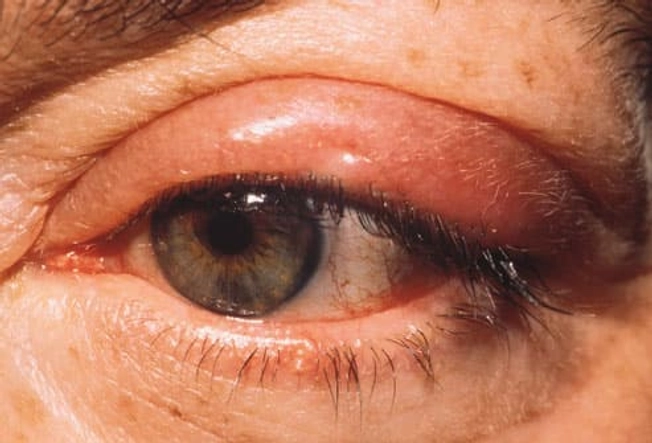
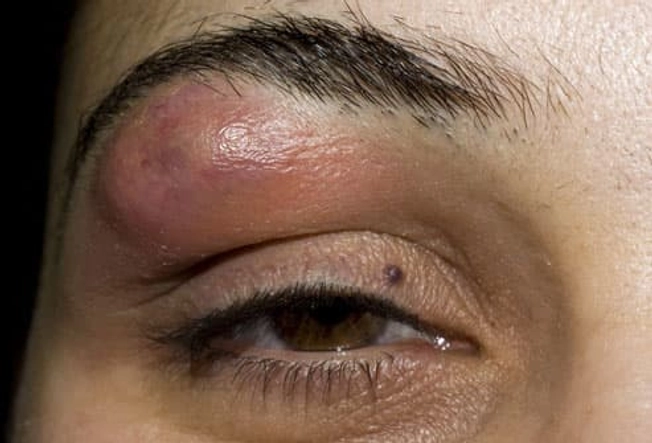
Boil Type: Stye
The familiar "stye on the eye" is a boil, usually caused by staph bacteria. It starts in the follicle of an eyelash and may be red, warm, swollen, and uncomfortable. A stye is sometimes confused with a chalazion, which is also a lump on the eyelid, but a chalazion is usually painless and is caused by a blocked oil gland, not an infection.

Who Gets Boils?
Anyone can develop a boil. The risk increases with:
- Close contact with an infected person
- Acne, eczema, or other causes of breaks in the skin
- Diabetes
- A weakened immune system

Treatment: Home Care
You can take care of most boils at home. Apply warm, moist compresses several times a day to help a boil open and drain. After it starts draining, keep it clean, and continue using warm compresses -- a clean one every time. Change the bandage often and wash hands well. Resist the urge to squeeze or pop the boil. This can make the infection worse.
When to Call the Doctor
If a boil doesn't heal after a week of home care, call your doctor. Other reasons to call include:
- A boil on the face or spine
- A fever or red streaks coming from the sore
- A very large or painful boil
- A boil that keeps coming back

Treatment: Procedures
If the fluid inside a boil doesn't drain by itself, your doctor may prick the top of the sore with a sterile instrument to be sure it drains completely. A deep infection may be packed with sterile gauze so it continues to drain. Antibiotics and steroid shots are sometimes given to help with healing.
Treatment: Recurrent Boils
For some people, boils are a recurring problem. In addition to standard treatment, your doctor may try to eliminate or reduce staph bacteria throughout the body. This can include any or all of the following treatments: washing up with a special antiseptic soap, using an antibiotic ointment inside the nose, or, if necessary, 1-2 months of antibiotics taken by mouth.
Boil Complications
Most boils heal with home treatment or a doctor's visit. Sores on the face may require antibiotics because they're so close to the eyes and brain. Rarely, the staph bacteria from a boil or carbuncle can get into the bloodstream, which can then affect the heart and other internal organs.

How to Prevent Boils
Since bacteria are everywhere in our environments and on many people's skin, the best defense against boils includes:
- Hand washing or use of alcohol-based hand sanitizer
- Careful cleaning of cuts, scrapes, and other wounds
- Keeping wounds covered
- Not sharing towels, sheets, razors, etc.
Wash towels, sheets, and anything else in contact with an infected area in very hot water. Throw away any wound dressings in a tightly sealed bag.