Phlebitis Overview
Phlebitis (fle-BYE-tis) means inflammation of a vein. Thrombophlebitis is due to one or more blood clots in a vein that cause inflammation. Thrombophlebitis usually occurs in leg veins, but it may occur in an arm or other parts of the body. The thrombus in the vein causes pain and irritation and may block blood flow in the veins. Phlebitis can occur in both the surface (superficial) or deep veins.
- Superficial phlebitis affects veins on the skin surface. The condition is rarely serious and, with proper care, usually resolves rapidly. Sometimes people with superficial phlebitis also get deep vein thrombophlebitis, so a medical evaluation is necessary.
- Deep vein thrombophlebitis affects the larger blood vessels, usually deep in the legs. Large blood clots can form, which may break off and travel to the lungs. This is a serious condition called pulmonary embolism.
Phlebitis Causes
Superficial phlebitis can be a complication due to a medical or surgical procedure.
Injury to a vein increases the risk of forming a blood clot. Sometimes clots occur without an injury. Some risk factors for thrombophlebitis include the following:
- Prolonged inactivity - Staying in bed or sitting for many hours, as in a car or on an airplane, creating stagnant or slow flow of blood from the legs in a dependent position (This pooling of blood in the legs leads to thrombus formation.)
- Sedentary lifestyle - Not getting any exercise
- Obesity
- Smoking cigarettes
- Certain medical conditions, such as cancer or blood disorders, that increase the clotting potential of the blood
- Injury to your arms or legs
- Hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills
- Pregnancy
- Varicose veins
Phlebitis Symptoms
Superficial phlebitis
There is usually a slow onset of a tender red area along the superficial veins on the skin. A long, thin red area may be seen as the inflammation follows a superficial vein. This area may feel hard, warm, and tender. The skin around the vein may be itchy and swollen. The area may begin to throb or burn.
Symptoms may be worse when the leg is lowered, especially when first getting out of bed in the morning. A low-grade fever may occur. Sometimes phlebitis may occur where a peripheral intravenous line was started. The surrounding area may be sore and tender along the vein.
If an infection is present, symptoms may include redness, fever, pain, swelling, or breakdown of the skin.
Deep vein phlebitis
This can be similar in presentation to superficial phlebitis, but some people may have no symptoms.
One may have pain and swelling throughout the entire limb. For example, the lower leg may swell for no apparent reason. Some people also get fever from a superimposed bacterial infection and skin discoloration or ulcers if the condition becomes chronic and was inadequately treated earlier.
When to Seek Medical Care
Call your health care provider if you have signs and symptoms of swelling, pain, and inflamed superficial veins on the arms or legs. If you are not better in a week or two or if it gets any worse, get reevaluated to make sure you don't have a more serious condition.
Deep vein thrombophlebitis requires immediate medical care. If you have any of these signs and symptoms, go to a hospital emergency department for evaluation:
- High fever with any symptoms in an arm or leg
- Lumps in a leg
- Severe pain and swelling in an arm or leg
- New, unexplained shortness of breath, which could be the first tip-off that a blood clot has already traveled to your lung; call 911if you are having trouble breathing.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask questions about your symptoms.
D-dimer is a blood test that measures a substance that is released as a blood clot dissolves. If this blood test is negative, and you have no risk factors, then it is unlikely that you have a blood clot.
Ultrasound can detect clots or blockage of blood flow, especially in larger, more proximal (upper leg) veins. A small hand-held instrument (probe) is pressed against your skin to help identify blood clots and where the obstruction is. This is a painless, noninvasive test.
Occasionally a venogram is needed to identify blood clots in the smaller, more distal veins. This is an invasive procedure that requires injecting X-ray dye or contrast material into a vein on the foot, then an X-ray is taken of the flow of the dye up the leg.
Phlebitis Treatment Self-Care at Home
An anti-inflammatory drug, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, can help lessen the pain and inflammation of superficial phlebitis. But check with your doctor first.
If you increase your walking, you increase blood flow. This helps prevent blood clots from developing.
Prescription leg compression stockings (knee or thigh high) improve your blood flow and may help to relieve your pain and swelling.
Avoid bed rest for prolonged periods. It can make your symptoms worse.
If you have deep vein thrombophlebitis, you may need to stay in the hospital for a few days for diagnosis and treatment to ensure that no complications occur.
Medical Treatment
If your evaluation shows superficial phlebitis and you are otherwise healthy, you can likely go home. You will need to use compression stockings and probably anti-inflammatory medications to control your symptoms. Additional management involves elevation of the arm/leg and application of warm compresses. Only a few cases require antibiotics.
If you have a history of deep vein thrombophlebitis, or if the phlebitis might possibly spread to the deep veins, you will need to take a blood thinner (anticoagulant). The duration of anticoagulant treatment is usually between 3-6 months or 3-12 months if this is the first time you've had DVT.
If you have signs of infection, you will need to take an antibiotic.
If the superficial phlebitis has progressed to involve the deep veins, then it is a serious condition that may even require hospital admission for treatment and further evaluation.
Next Steps Outlook
Phlebitis in the superficial veins is rarely serious and usually responds to pain control, elevation, and warm compresses for 1-2 weeks.
Multimedia
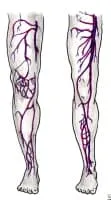
Media file 1: Superficial and deep vein systems in the leg.
Synonyms and Keywords
phlebitis, blood clot in the arm, blood clot in the leg, deep venous thrombophlebitis, thrombophlebitis, superficial vein thrombophlebitis, superficial phlebitis, thrombus, inflammation of a vein, deep vein thrombophlebitis

