- Screening & Tests
- Diet & Exercise
- Rest & Relaxation
- Reproductive Health
- Head to Toe
- View Full Guide
Slideshow: What's Causing Your Pelvic Pain?

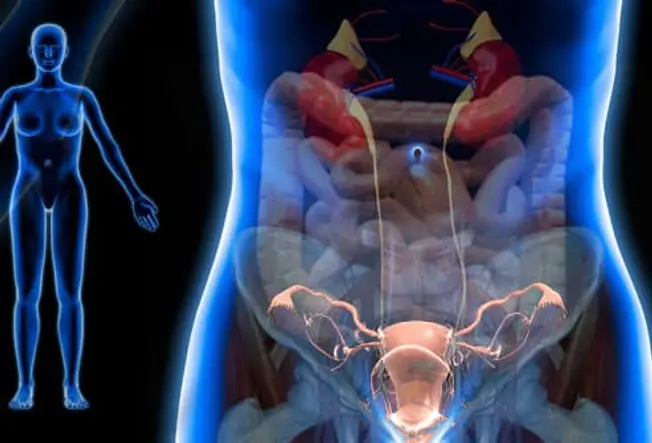
What Is Pelvic Pain?
If you have pain below your belly button and above your legs, it counts as pelvic pain. It can be caused by a lot of things. It may be a harmless sign that you’re fertile, a digestive disorder, or a red flag that you need to go to the hospital.
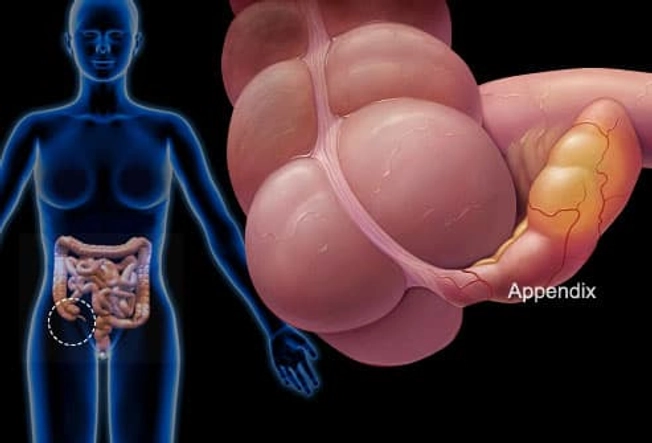
Appendicitis
If you have a sharp pain in the lower right part of your belly, are vomiting, and have a fever, it could be appendicitis. If you have these symptoms, go to the ER. An infected appendix may need surgery. If it bursts, it can spread the infection inside your body. This can cause serious complications.
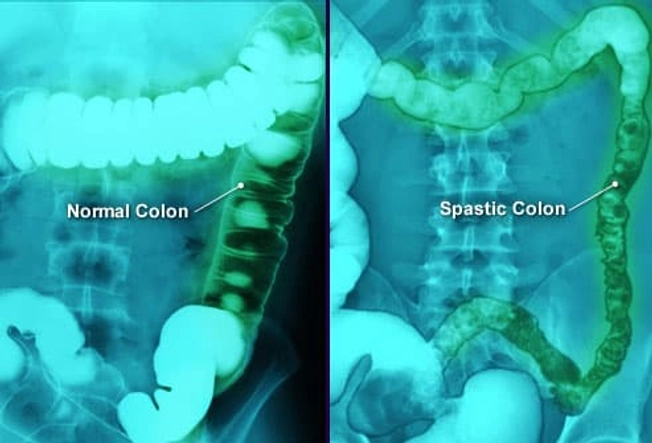
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Do you have belly pain, cramps, bloating, and diarrhea or constipation that keeps coming back? Talk to your doctor to figure out the problem. It could be IBS, sometimes called spastic colon. Doctors aren’t sure what causes it. Diet changes, stress management, and medications may help.
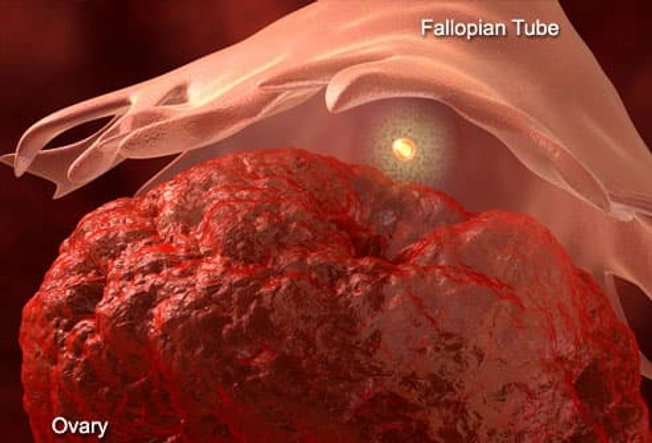
Mittelschmerz (Painful Ovulation)
Ever feel a painful twinge between periods? You may be feeling your body ovulate. When you do, the ovary releases an egg along with some fluid and blood. It can cause irritation. This feeling is called mittelschmerz -- German for "middle" and "pain." That’s because it happens midway through your monthly cycle. The pain may switch sides from month to month. It isn't harmful and usually goes away in a few hours.
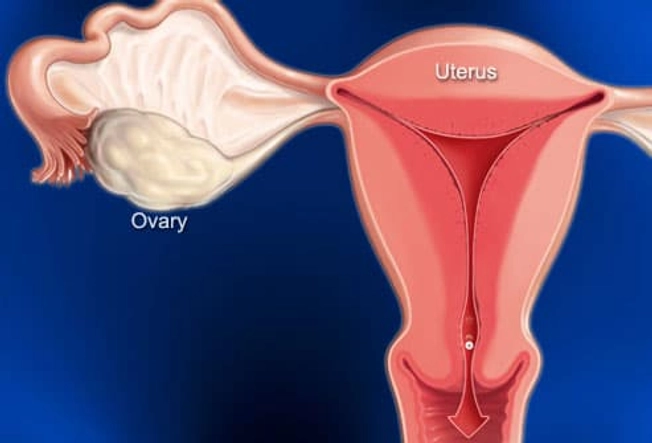
PMS and Menstrual Cramps
You can usually feel these cramps in your lower belly or back. They typically last 1 to 3 days. Why the pain? Every month, your uterus builds up a lining of tissue. That’s where an embryo can implant and grow. If you don't get pregnant, the lining breaks down and is shed during your period. When the uterus tightens to push it out, you get a cramp. Try a heating pad and over-the-counter pain relievers to ease pain. Exercise and de-stressing can help, too. You can also talk to your doctor about PMS pain. Certain birth control pills or antidepressants may help.
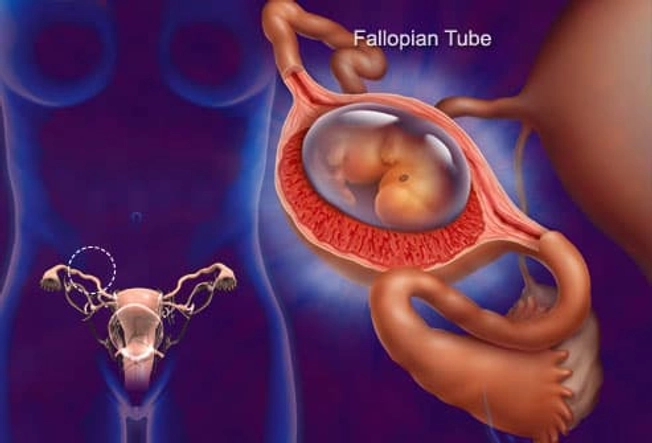
Ectopic Pregnancy
This happens when an embryo implants somewhere outside of the uterus and begins to grow. This usually happens in the fallopian tubes. Sharp pelvic pain or cramps (particularly on one side), vaginal bleeding, nausea, and dizziness are symptoms. Get medical help right away. This is a life-threatening emergency.
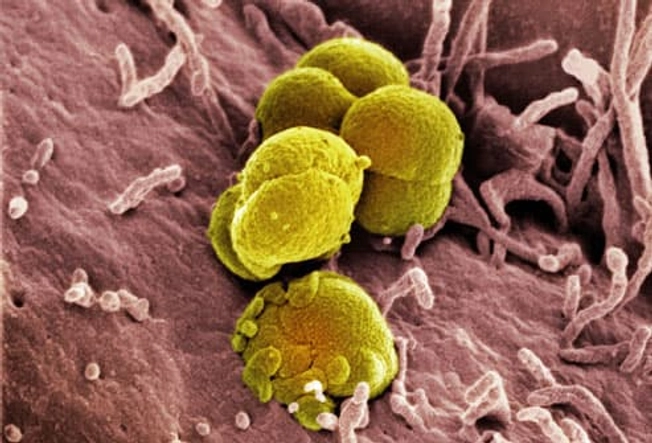
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Pelvic pain is a warning sign of some STDs. Two of the most common are chlamydia and gonorrhea (shown here through a microscope). You often get both at the same time. They don't always cause symptoms. But when they do, you may have pain when you pee, bleeding between periods, and abnormal vaginal discharge. See your doctor. It’s also important to get partners checked and treated, too, so you don’t pass the infection back and forth.
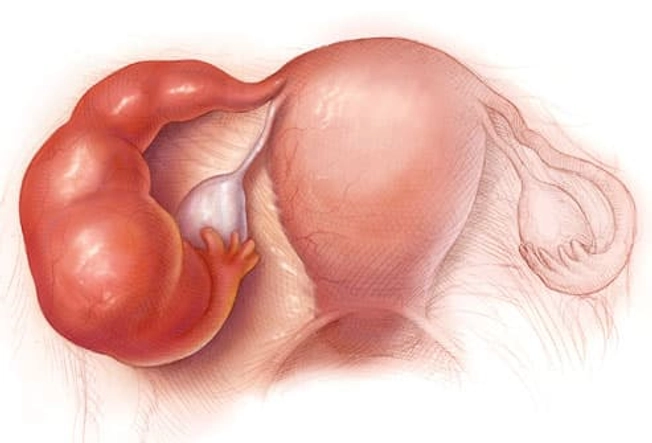
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
This is a complication of sexually transmitted diseases. It's the No. 1 preventable cause of infertility in women. It can cause permanent damage to the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Belly pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and pain during sex or urination can be symptoms. Get it treated right away to avoid damage. It is treated with antibiotics. In severe cases, you may need to be hospitalized. Get your partner treated, too.
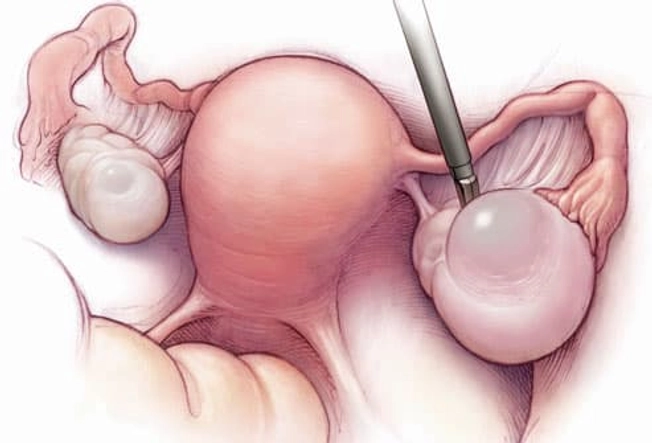
Ovarian Cysts
Ovaries release eggs when you ovulate. Sometimes a follicle doesn't open to release the egg. Or it recloses after it does and swells with fluid. This causes an ovarian cyst. They’re usually harmless and go away on their own. But they may cause pelvic pain, pressure, swelling, and bloating. And if a cyst bursts or twists, it can cause sudden, severe pain, sending you to the emergency room. Doctors can spot them during a pelvic exam or ultrasound.
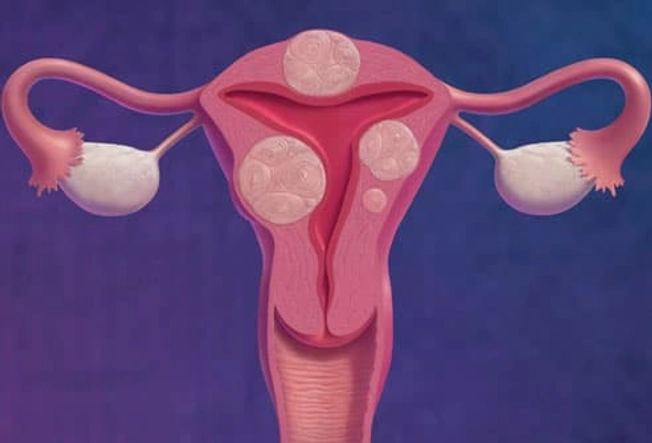
Uterine Fibroids
These grow on or in the wall of the uterus. While they’re sometimes called fibroid tumors, they're not cancerous. Fibroids are common in women in their 30s and 40s. They usually don’t cause problems. But some women may have pressure in the belly, low back pain, heavy periods, painful sex, or trouble getting pregnant. Your doctor can suggest treatments to relieve your symptoms or to shrink or remove fibroids.
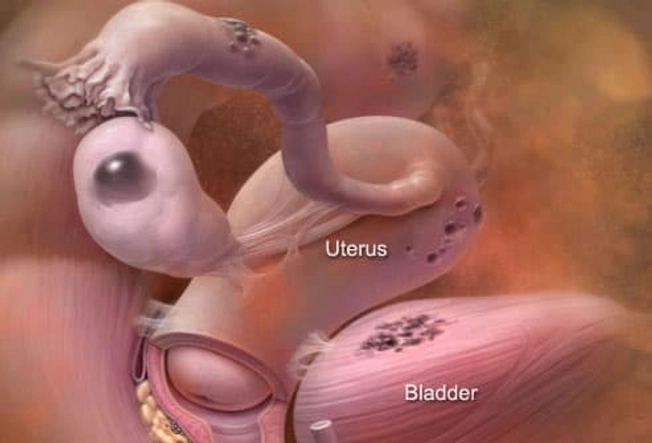
Endometriosis
Some women have tissue growing outside the uterus that's similar to the tissue that lines the uterus. It can grow on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, intestines, and other parts of the body. When it's time for your period, these clumps of tissue break down. But the tissue has no way to leave your body. While this is rarely dangerous, it can cause pain and form scar tissue that may make it tough to get pregnant. There are several treatment options. Pain medications, birth control pills, hormone medications to stop or reduce periods, surgery with small cuts, and even a hysterectomy (surgery to take out your uterus) are options.
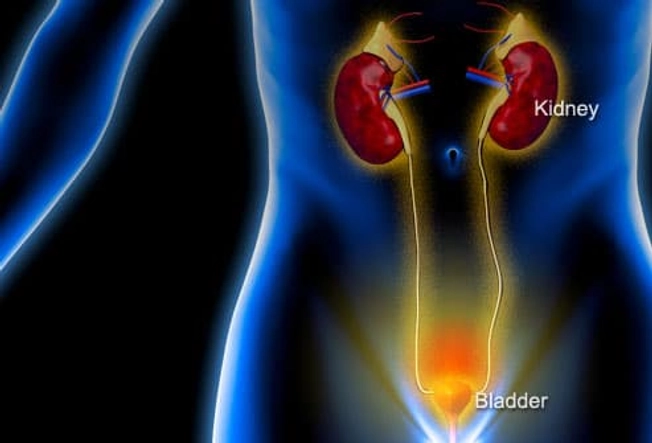
Urinary Tract Infection
Do you have to pee often, or does it hurt when you do? Or do you feel like your bladder is full? It could be a UTI. This happens when germs get into your urinary tract. Treating it quickly can keep it from it getting serious. But if it spreads to the kidneys, it can cause serious damage. Signs of a kidney infection include fever, nausea, vomiting, and pain in one side of the lower back.
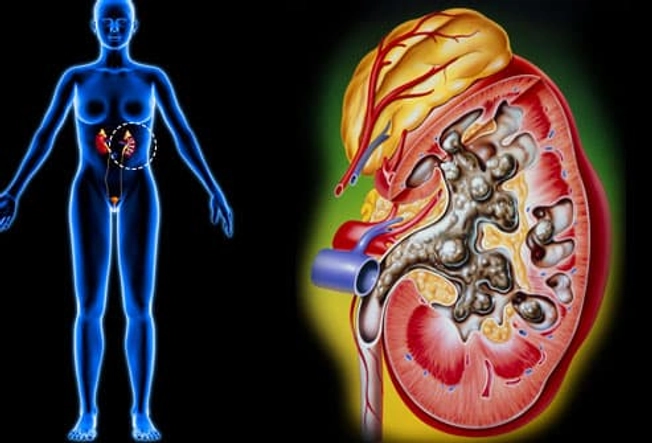
Kidney Stones
These are globs of salt and minerals that your body tries to get rid of in urine. They can be as tiny as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. And boy can they hurt! Your urine may turn pink or red from blood. See your doctor if you think you have a kidney stone. Most will pass out of your system on their own, but some need treatment. Even if they can pass on their own, your doctor can help with pain medication and will tell you to drink lots of water.
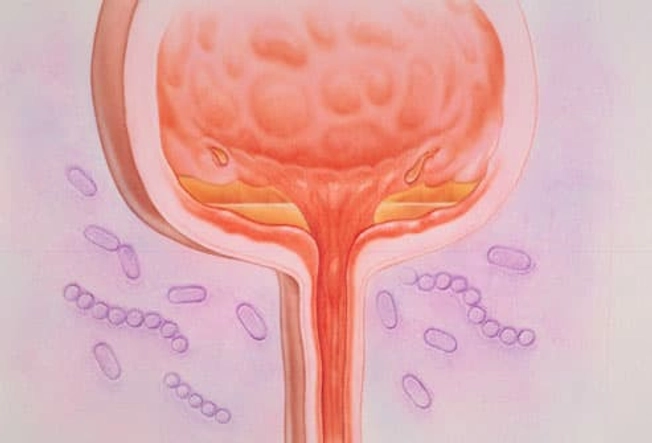
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
This condition causes ongoing pain and is related to inflammation of the bladder (illustrated here). It’s most common in women in their 30s and 40s. Doctors aren’t sure why it happens. People with severe IC may need to pee several times an hour. You might also feel pressure above the pubic area, pain when you urinate, and pain during sex. Although this can be a long-term condition, there are ways to ease the symptoms and avoid flares.
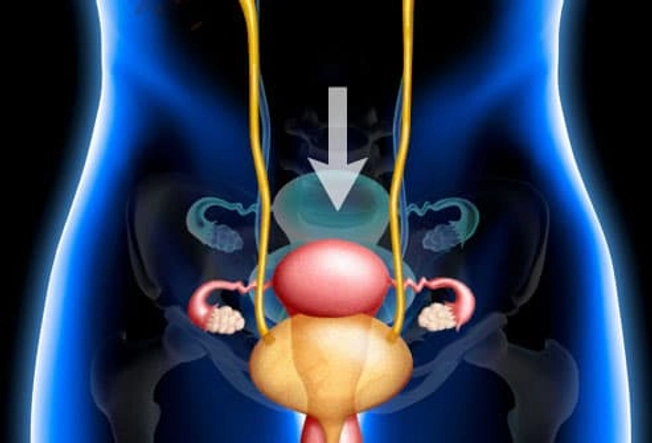
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
As you get older, this may happen. Your bladder or uterus drops into a lower position. It usually isn't a serious health problem, but it can be uncomfortable. You may feel pressure against the vaginal wall, or your lower belly may feel full. It may also give you an uncomfortable feeling in the groin or lower back and make sex hurt. Special exercises like Kegel’s or surgery may help.
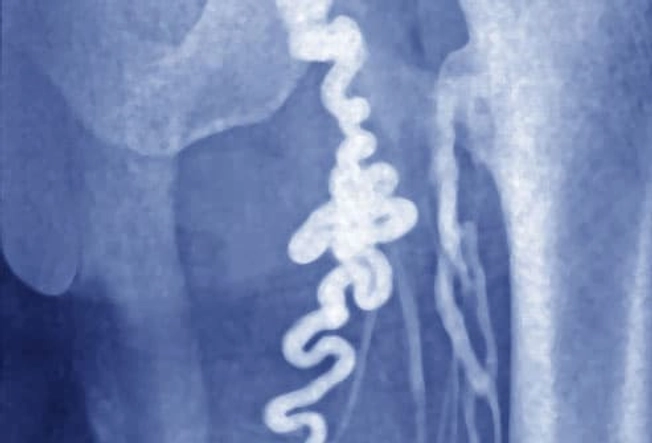
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
We’ve all seen varicose veins in legs. (This is a picture of one in the upper thigh.) They can sometimes happen in the pelvis, too. When blood backs up in veins, they become swollen and painful. This is known as pelvic congestion syndrome. This is a condition that's difficult to diagnose and treat. It tends to hurt worse when you sit or stand. Lying down may feel better. But because the best treatment is still unclear, you need to work with your doctor to learn what the options are and to find what works well for you.
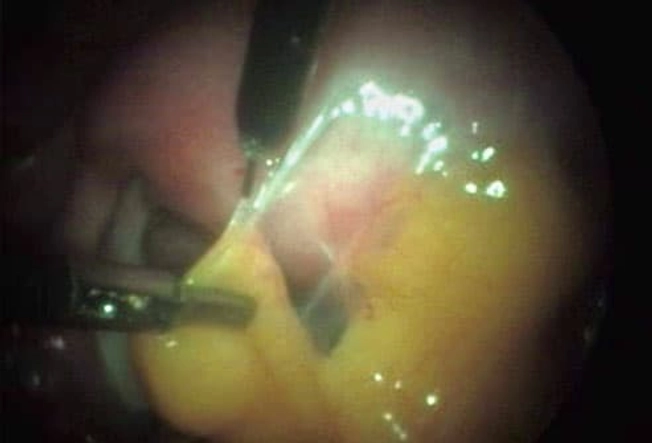
Scar Tissue
If you've had surgery or an infection, you could have ongoing pain from this. Adhesions are a type of scar tissue inside your body. They form between organs or structures that aren’t meant to be connected. Adhesions in your belly can cause pain and other problems, depending on where they are. In some cases, you may need a procedure or surgery to get rid of them.
Vulvodynia
Does it hurt when you ride a bike or have sex? If it burns, stings, or throbs around the opening of your vagina, it could be this. The feelings can be ongoing or come and go. Before you’re diagnosed with this, your doctor will rule out other causes. This isn’t caused by an infection. Treatment options range from medication to physical therapy.

Painful Sex
This can be caused by many things. Most are treatable. It could be a vaginal infection, or you just may need more lubrication. The medical name is dyspareunia. Sometimes the pain gets better after sexual therapy. This type of talk therapy can focus on inner conflicts about sex or past abuse.
Chronic Pelvic Pain
If you have pain that lasts at least 6 months, it’s considered chronic. It may be so bad it messes with your sleep, career, or relationships. See your doctor. Most of the conditions we've covered get better with treatment. Sometimes, even after a lot of testing, the cause of pelvic pain remains a mystery. But your doctor can still help you find ways to feel better.