- Overview
- Alcohol Use Disorder
- Opioid Use Disorder
- Cannabis Use Disorder
- Prescription Drug Abuse
- Other Abused Substances
- Non-Substance Addictions
- View Full Guide
Alcohol and the Aging Process


A Bad Mix
Alcohol is linked to age in lots of ways. You have to be old enough to drink it legally, and once you are, it can age you faster than normal. Heavy drinking can have a direct effect on certain parts of your body and on your mental health as you get older. And it can have some unhealthy indirect effects, as well.

It Can Dehydrate You
As you get older, you have less water in your body and -- for reasons that aren’t quite clear --you also feel thirsty less often. That makes seniors more likely to be dehydrated. Drinking alcohol can pull more water out of your body and make your chances of dehydration even higher.
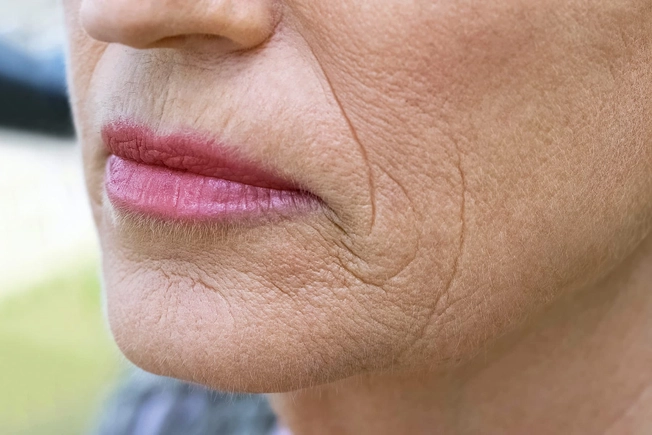
It Can Dry Your Skin
Our skin gets thinner and drier as we age. It’s a natural process called intrinsic aging, and it’s something you can’t control. Extrinsic aging is when your skin ages faster than it should because of your environment and how you live. That’s where alcohol comes in -- it dehydrates you and dries out your skin. You can slow that down by drinking less.
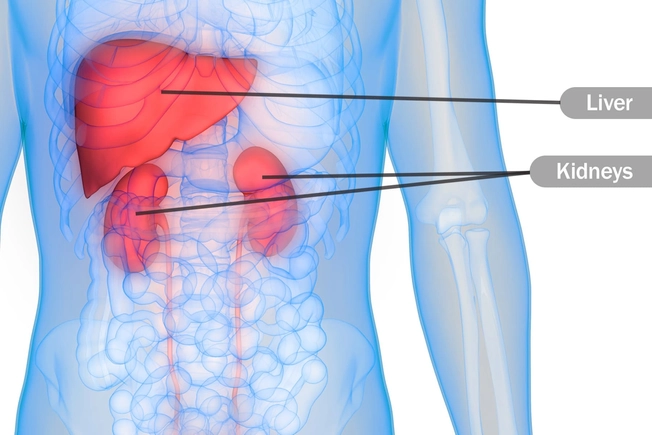
It Can Make Vital Organs Weaker
Alcohol can affect the way some vital organs work and make them age faster. While heavy drinkers are more likely to have cirrhosis (permanent damage to your liver), even moderate drinking can lead to problems like fatty liver disease. It also can make it harder for your kidneys to do their thing.
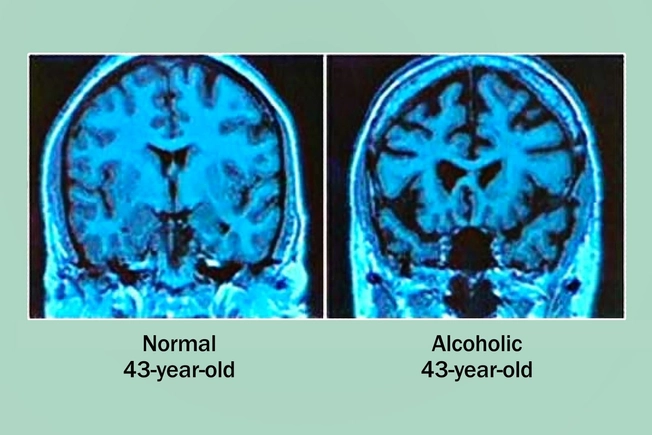
It Can Slow Your Brain
Every alcoholic drink goes “straight to your head,” or at least to your brain. Heavy drinking over a long time can shrink brain cells and lead to alcohol-related brain damage (ARBD) and certain types of dementia. Symptoms of that include lack of judgment, organization, or emotional control, trouble staying focused, and anger issues.
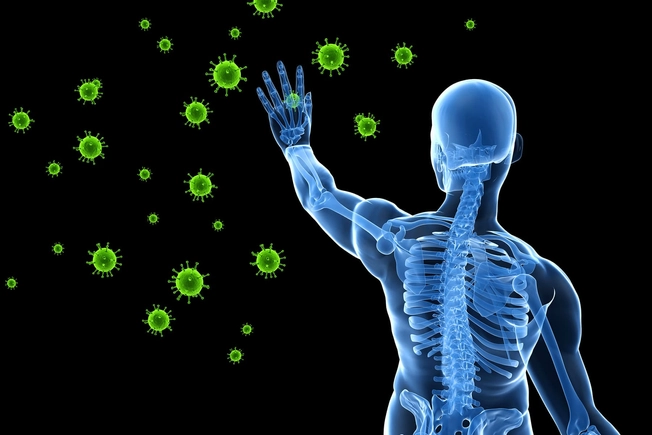
It Can Weaken Your Immune System
Alcohol can affect the way your body fights off life-threatening illnesses like tuberculosis or pneumonia. This can be especially serious for older people. Researchers are also studying the possibility that alcoholic liver disease might be caused, at least in part, by your immune system attacking healthy body tissues.
It Can Affect Your Heart
Red wine has antioxidants called polyphenols that may help your cholesterol level and protect your blood vessels. If you drink it in moderation (about one glass a day), some studies show that it might be good for your heart. But too much can lead to an abnormal heartbeat and high blood pressure. So if you don’t drink, this isn’t a good reason to start.

It Hits You Faster
People who drink may notice that they’re “feeling no pain” sooner as they get older. That’s mainly because our bodies gain fat and lose muscle in our senior years and it takes longer for us to break down alcohol and get it out of our system. It also can make hangovers last longer.

It Can Complicate Things
Alcohol may not only make you more likely to get sick as you age, it also can make common medical problems worse. Studies show that heavy drinkers can have a harder time with things like osteoporosis, diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, ulcers, cancer, memory loss, and certain mood disorders.
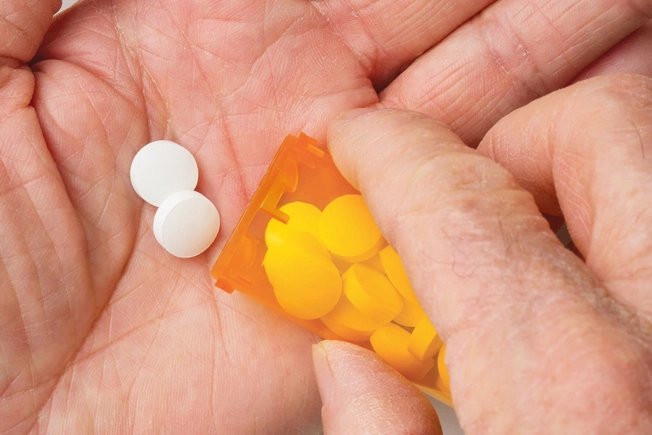

It Can Change How Your Meds Work
The older you get, the longer alcohol stays in your system. So it’s more likely to be there when you take medicine. And alcohol can affect the way your meds work. It can also lead to serious side effects.
For example, drinking alcohol when you take aspirin can raise your chances of stomach problems or internal bleeding. Mixing it with certain sleeping pills, pain medications, or anxiety drugs can be life-threatening.

It Can Make You More Likely to Fall
Broken bones from a stumble are a serious health issue for seniors. Heavy drinking can make them even more likely. It’s because alcohol can affect your balance and sense of judgment. Over time, it also can damage the cerebellum, the area in your brain that handles balance and coordination.

It Can Keep You Up at Night
The idea of having a drink to relax before bedtime may not be a good one, especially as you get older. Instead of lulling you into a restful night, alcohol can actually keep you from getting to sleep and lead to restless slumber. That can be particularly hard on seniors, who are already more likely to wake up often or have a sleep disorder like insomnia.
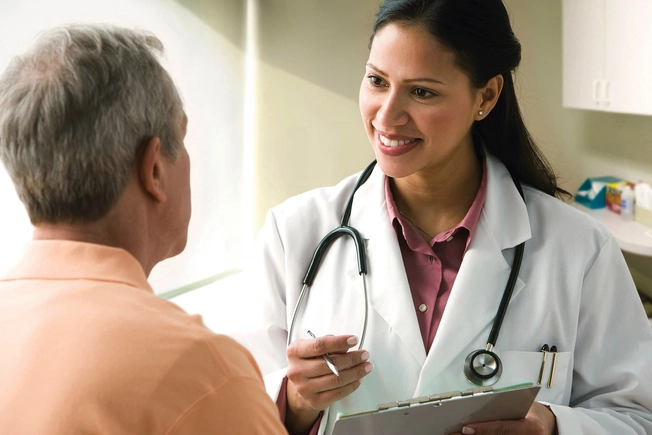

You Can Drink, But ...
As with most things, moderation is key. People older than 65 who don’t take any medications should average no more than one drink a day (seven per week) and have no more than three at one sitting. (A drink is one 12-ounce can or bottle of beer, one 5-ounce glass of wine, or one 1.5-ounce shot of an 80-proof or less liquor.) Talk with your doctor to find out what’s right for you.