What’s a Ketogenic Diet?
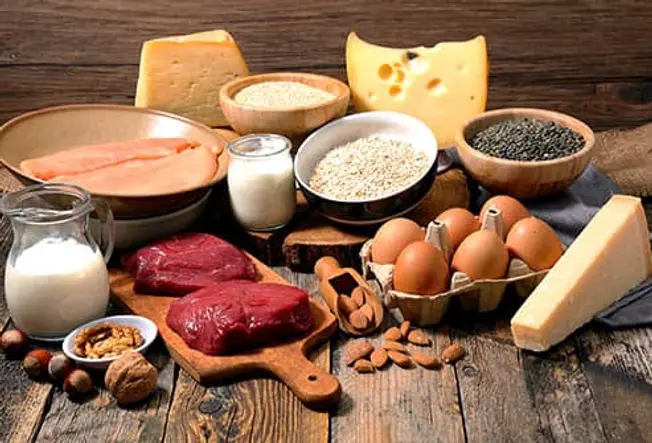


What Is It?
“Ketogenic” is a term for a low-carb diet (like the Atkins diet). The idea is for you to get more calories from protein and fat and less from carbohydrates. You cut back most on the carbs that are easy to digest, like sugar, soda, pastries, and white bread.

How It Works
When you eat less than 50 grams of carbs a day, your body eventually runs out of fuel (blood sugar) it can use quickly. This typically takes 3 to 4 days. Then you’ll start to break down protein and fat for energy, which can make you lose weight. This is called ketosis. It's important to note that the ketogenic diet is a short term diet that's focussed on weight loss rather than the pursuit of health benefits.

Who Uses It?
People use a ketogenic diet most often to lose weight, but it can help manage certain medical conditions, like epilepsy, too. It also may help people with heart disease, certain brain diseases, and even acne, but there needs to be more research in those areas. Talk with your doctor first to find out if it’s safe for you to try a ketogenic diet, especially if you have type 1 diabetes.

Weight Loss
A ketogenic diet may help you lose more weight in the first 3 to 6 months than some other diets. This may be because it takes more calories to change fat into energy than it does to change carbs into energy. It’s also possible that a high-fat, high-protein diet satisfies you more, so you eat less, but that hasn’t been proved yet.
Cancer
Insulin is a hormone that lets your body use or store sugar as fuel. Ketogenic diets make you burn through this fuel quickly, so you don’t need to store it. This means your body needs -- and makes -- less insulin. Those lower levels may help protect you against some kinds of cancer or even slow the growth of cancer cells. More research is needed on this, though.

Heart Disease
It seems strange that a diet that calls for more fat can raise “good” cholesterol and lower “bad” cholesterol, but ketogenic diets are linked to just that. It may be because the lower levels of insulin that result from these diets can stop your body from making more cholesterol. That means you’re less likely to have high blood pressure, hardened arteries, heart failure, and other heart conditions. It's unclear, however; how long these effects last.
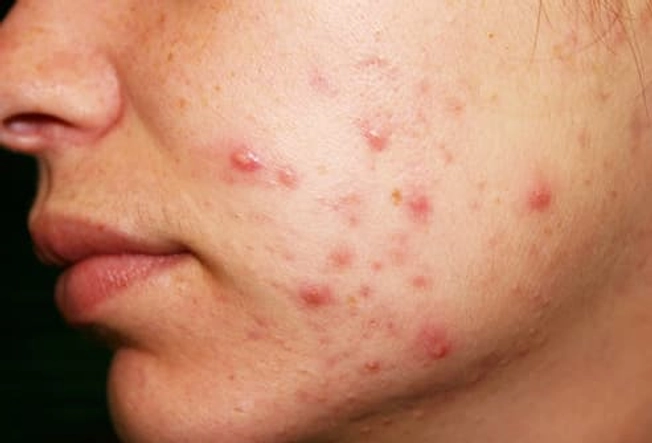
Acne
Carbohydrates have been linked to this skin condition, so cutting down on them may help. And the drop in insulin that a ketogenic diet can trigger may also help stop acne breakouts. (Insulin can cause your body to make other hormones that bring on outbreaks.) Still, more research is needed to determine exactly how much effect, if any, the diet actually has on acne.
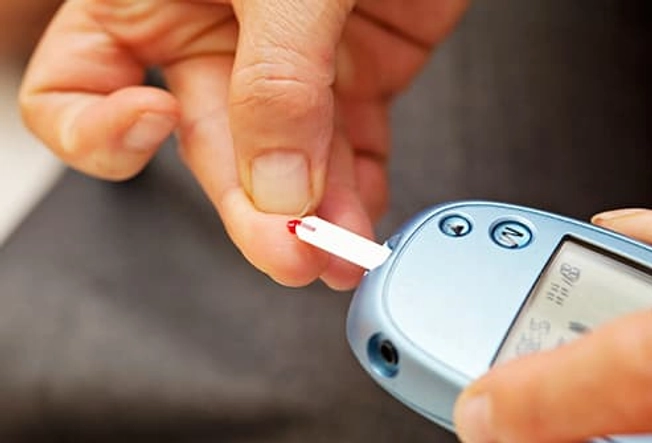

Diabetes
Low-carb diets seem to help keep your blood sugar lower and more predictable than other diets. But when your body burns fat for energy, it makes compounds called ketones. If you have diabetes, particularly type 1, too many ketones in your blood can make you sick. So it’s very important to work with your doctor on any changes in your diet.
Epilepsy
Ketogenic diets have helped control seizures caused by this condition since the 1920s. But again, it’s important to work with your doctor to figure out what’s right for you or your child.
Other Nervous System Disorders
These affect your brain and spine, as well as the nerves that link them together. Epilepsy is one, but others may be helped by a ketogenic diet as well, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and sleep disorders. Scientists aren’t sure why, but it may be that the ketones your body makes when it breaks down fat for energy help protect your brain cells from damage.
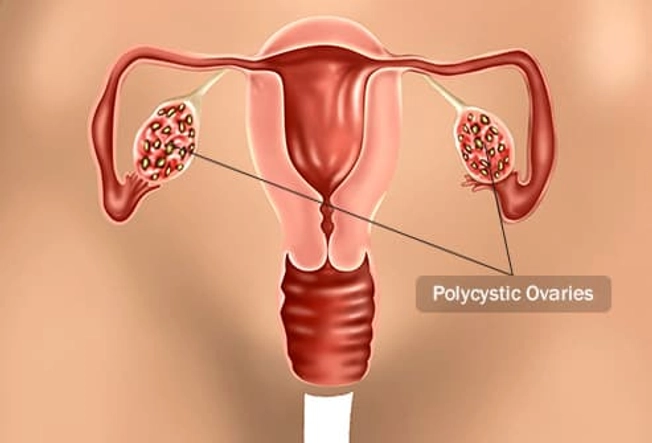
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
This is when a woman’s ovaries get larger than they should be and small fluid-filled sacs form around the eggs. High levels of insulin can cause it. Ketogenic diets, which lower both the amount of insulin you make and the amount you need, may help treat it, along with other lifestyle changes, like exercise and weight loss.

Exercise
A ketogenic diet may help endurance athletes -- runners and cyclists, for example -- when they train. Over time, it helps your muscle-to-fat ratio and raises the amount of oxygen your body is able to use when it’s working hard. But while it might help in training, it may not work as well as other diets for peak performance.
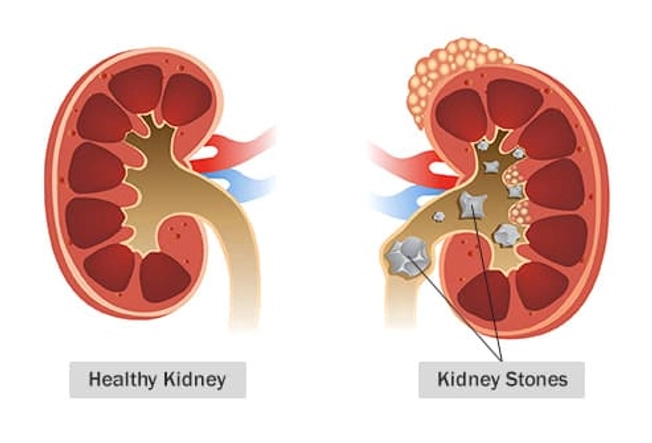
Side Effects
The more common ones aren’t usually serious: You might have constipation, mild low blood sugar, or indigestion. Much less often, low-carb diets can lead to kidney stones or high levels of acid in your body (acidosis). Other side effects can include the "keto flu," which may include headache, weakness, and irritability; bad breath; and fatigue.

Diet With Care
When your body burns its stores of fat, it can be hard on your kidneys. And starting a ketogenic diet -- or going back to a normal diet afterward -- can be tricky if you’re obese because of other health issues you’re likely to have, like diabetes, a heart condition, or high blood pressure. If you have any of these conditions, make diet changes slowly and only with the guidance of your doctor.
