Why You Need Zinc and How to Get It

What Is Zinc?
It’s a mineral your cells need to fight off bacteria and viruses and make the genetic material, called DNA, that tells your body how to work the way it should. It helps you heal wounds, aids your senses of smell and taste, and is important for infants and children as they grow.

How Much Do You Need?
An adult man needs 11 milligrams a day, and an adult woman, 8 milligrams. If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, you’ll need more -- around 12 milligrams. Children need 2 to 11 milligrams depending on their age and gender. Talk to your pediatrician about how much is right for your child.

Do I Get Enough?
Probably, yes -- most Americans do. But some things can make it hard for your body to use it, including surgery on your stomach or intestines, alcohol abuse, and digestive diseases like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. And people who don’t eat meat or animal products can have a harder time getting enough zinc from food.

What Happens If I Don’t Get Enough?
It can make children grow more slowly and delay puberty in teens. Adults who are low on zinc can have hair loss, diarrhea, sores on their eyes and skin, and loss of appetite. It also can affect a man’s sexual desire. Talk to your doctor before taking a supplement, though. These issues can be caused by something other than a lack of zinc.

Healthy Skin
Zinc helps your skin do what it’s supposed to: protect you from heat and cold, bacteria, and viruses. Your doctor might prescribe a zinc supplement or ointment to treat certain skin problems, like acne.

Can It Cure the Common Cold?
Some studies suggest that if you take zinc lozenges or syrup -- but not pill supplements -- within 24 hours of feeling a cold coming on, your symptoms won’t be as bad or last as long. (Nasal sprays and gels that have it are linked to the loss of sense of smell.) More research is needed to figure out if it really works and, if so, how you should take it.
May Help Prevent Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
This is an eye disease that causes vision loss over time. A large study of people at higher risk of getting AMD showed that taking a daily multivitamin with zinc -- along with vitamins A and C, beta-carotene, and copper -- may help avoid it. But other studies haven’t had the same results. If you’re at higher risk, talk to your doctor to see if a vitamin would be a good idea for you.
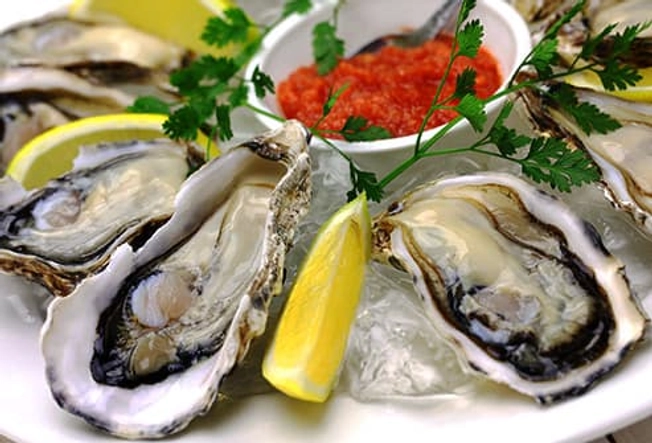

Source: Oysters
Nothing beats oysters for zinc. A 3-ounce serving has 74 milligrams. That’s five times more than you need per day. Eat them raw with a lemon or bake them Rockefeller-style with spinach, onions, breadcrumbs, and Parmesan cheese.
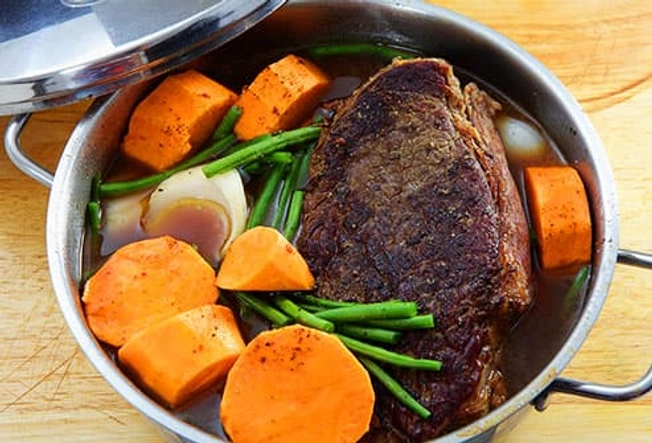

Source: Chuck Roast
Too much red meat -- especially fatty meat -- has been linked to health problems, but it can deliver some essential nutrients, including zinc. Just keep your portions small and eat plenty of green vegetables on the side. A 3-ounce serving has about 7 milligrams of zinc.
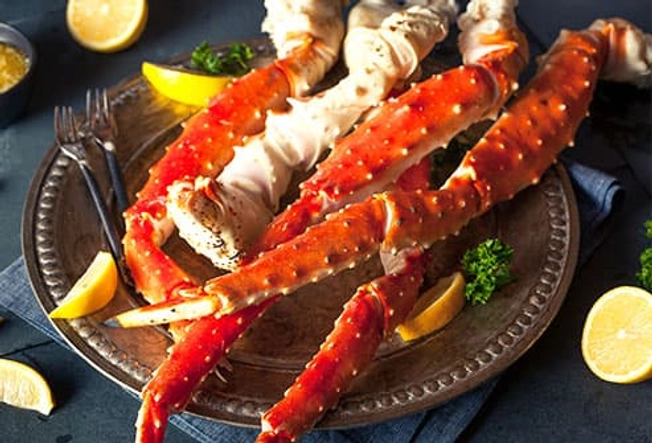

Source: Alaska King Crab
Slice a lemon and melt a little butter, and you’ll have a feast fit for a king. A 3-ounce serving has 6.5 milligrams of zinc. It takes a bit of practice to get the meat out of the shell, but that’s half the fun. Plus, it makes you eat more slowly, which is healthier because you’re less likely to overeat.
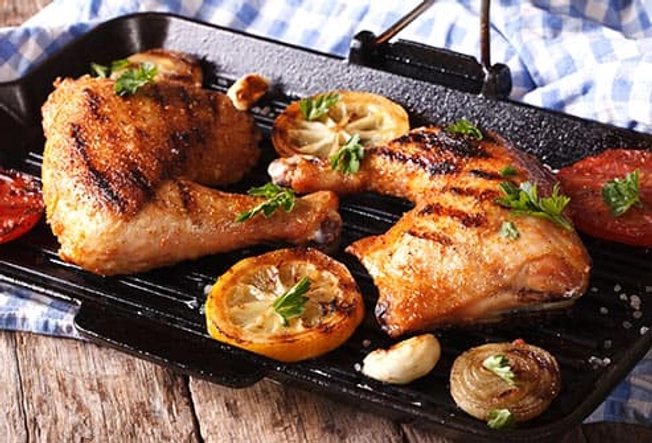

Source: Dark Meat Chicken
It has 2.4 milligrams of zinc per 3-ounce serving, compared with less than 1 milligram in a skinless chicken breast. Try some pan-roasted chicken thighs with sautéed kale for a healthy, tasty meal.
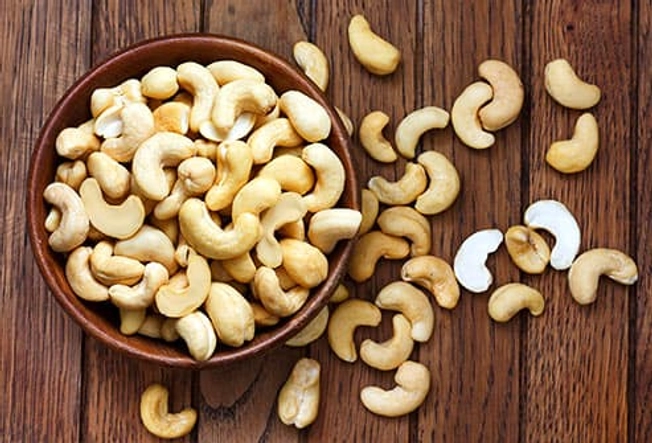

Source: Cashews
How about a zinc-rich snack? Cashews have 1.6 milligrams of zinc per 1-ounce serving. Keep them at your desk for a healthy treat instead of candy or chips. Just watch your portions. While they’re healthy, cashews are also full of calories and fat.
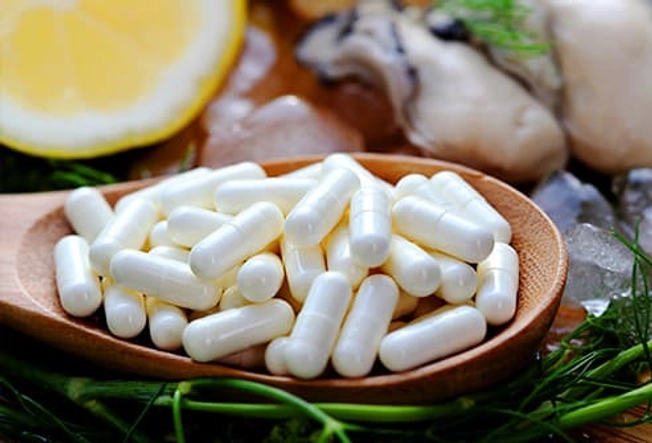

Zinc Supplements
Even though most Americans get enough zinc from their meat-rich diet, some people take more -- as a supplement by itself or as part of a multivitamin. This can be helpful if you don’t get enough in your diet or you have certain medical conditions, but it’s not always safe. Check with your doctor first.

Too Much Can Be Bad for You
It can cause diarrhea, stomach cramps, headache, and nausea. And if you take too much for too long, you may have lower levels of copper (another essential nutrient), a weaker immune system, and less HDL -- or “good” -- cholesterol. You shouldn’t get more than 40 milligrams a day unless your doctor has told you otherwise. Talk to your pediatrician before giving a zinc supplement to your child.

Interactions With Other Medication
Zinc supplements can weaken the effects of antibiotics, and antibiotics can make it harder for your body to use zinc. The supplements also can make it harder for your body to absorb some drugs, like the arthritis drug penicillamine. Talk to your doctor before taking a zinc supplement.
