Cardio Exercise: Good for More Than Your Heart


Heart Health Is Just the Start
You probably already know that cardio, or "aerobic," exercise -- the kind that gets your heart pumping -- is good for your ticker. It lowers your resting pulse and strengthens your heart muscle. That's why, as you slowly lengthen your cardio workouts, you're able to go for longer time and distance. But your heart isn't the only part of your body that benefits.

Lower Your Blood Sugar
Cardio exercise helps lower blood sugar (glucose) levels and improve insulin resistance if you have diabetes. Resistance training, like weightlifting, is also good. A combination of the two seems to help the most. Talk to your doctor before you start a new fitness routine if you have diabetes, especially if you take insulin or other meds.

Improve Your Mood
Aerobic exercise like running can help ease depression and anxiety well enough that your doctor or therapist may suggest it as a treatment. Part of the reason might be that it seems to enlarge your hippocampus -- an area of your brain that manages emotion -- and slow the breakdown of brain cells. Stick with it on a regular basis for several months to get the most benefit.

Get a Better Night's Sleep
Cardio may be good for your shut-eye. Scientists know that it can help you keep an even mood, wind down at bedtime, and set up a healthy sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm). The exact brain effects aren't always clear, but people who exercise more tend to get more of the deep "slow wave" sleep that helps renew the brain and body. But try not to exercise too close to bedtime, which disrupts sleep for some people.

Think Better
People who do more aerobic exercise may be better at "executive function" -- the ability to organize information, interpret it, and act on it. Just a single workout session can increase blood flow to the part of your brain called the prefrontal cortex, which helps control your executive function. Over the long term, exercise seems to help brain cells in your prefrontal cortex connect more easily.

Remember Better
People who move around more are less likely to get Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. That's in part because exercise helps prevent things that can raise your chances of getting dementia, such as obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and depression.

Learn Better
Neuroplasticity is the ability of your brain to change when you learn and do new things. Younger brains are generally better at this than older ones, but you can help preserve your neuroplasticity with cardio exercise, along with resistance training.
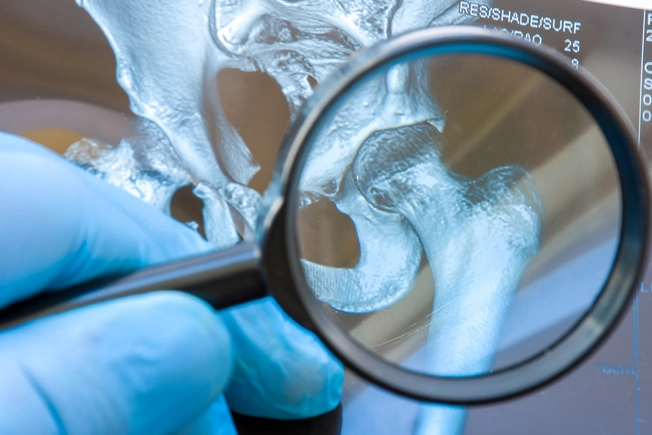
Help Ease Arthritis Pain
As you age, your knees and other joints can get osteoarthritis. The movement of aerobic exercise, like jogging or biking, is one of the most effective ways to ease pain and inflammation. And whether you walk, swim, or row a boat, your heart gets fitter, which makes it easier to stay active. When you combine physical activity with a healthy diet, you can drop extra pounds, which takes pressure off your knees.

Breathe Better
Even if you have a lung condition, regular cardio exercise can help improve your breathing. If the gym's not your thing, a walk, jog, or a regular tennis game can do the trick. Just make sure to talk to your doctor about your exercise plan if you already have breathing problems.
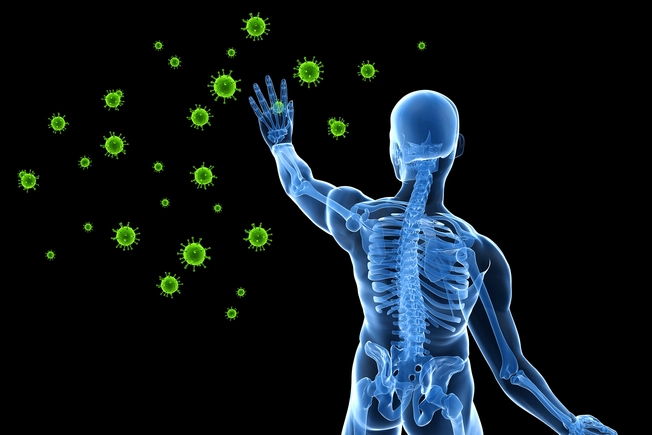
Help Fight Germs
Regular aerobic exercise appears to help your body fight illness caused by viruses and bacteria. That's partly because it helps blood get around your body better, which means germ-fighting substances get where they need to go. Scientists continue to study exactly how exercise helps boost the immune system -- your body's defense against germs.
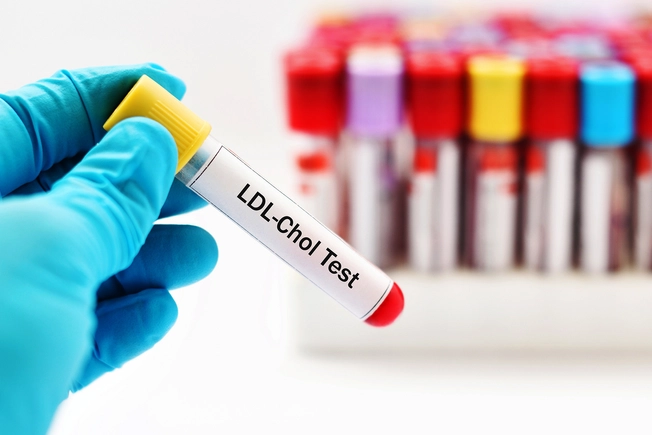
Improve Your Cholesterol
Exercise seems to raise your HDL "good" cholesterol. It can also lower your LDL "bad" cholesterol, though you may need to make your workout more intense to get the full effect. Unhealthy cholesterol numbers make you more likely to build up plaque in your arteries that can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Talk to your doctor about starting a fitness routine if you're already ill or you haven't exercised in a while.

How Much Exercise Is Right?
Standard recommendations call for 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week. That's a great place to start. But upping that to 300 minutes a week or higher can add even more benefits. The length of each session matters, too. Some of the best brain benefits come in exercise periods that last a bit longer: 45 to 60 minutes.
