What to Eat Before and After a Workout


Power Up
The right foods before and after exercise can boost your results. Like a car uses gas, your body burns carbohydrates for fuel. They give you the energy to power through that jog or fitness class. When you’re done, refueling with a combination of protein and carbs can help you rebuild muscle. Ready to make the most of your workout?

Time It Right
Aim to have a snack or mini meal 1 to 3 hours before your workout. You can have tummy troubles if you chow down right before. That’s because more blood goes to your muscles during exercise, leaving less for digestion. After exercise, your body is ready to refuel and rebuild muscle tissue. Eat or drink within an hour of finishing.
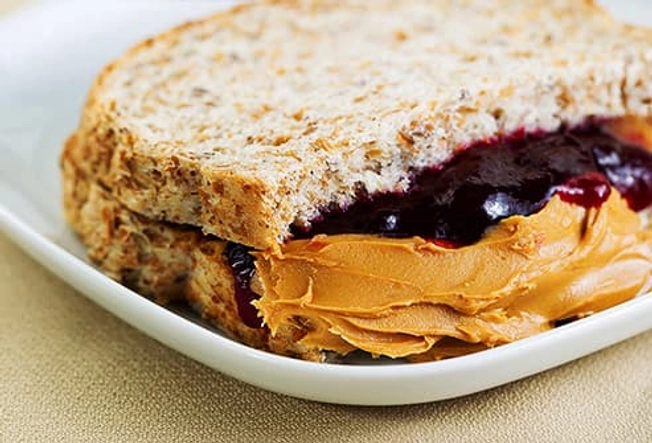

Before: PB&J
The bread and jelly in this lunchbox staple serve up the carbs. They give you the energy your muscles need during exercise. The peanut butter adds a dose of protein, which helps you feel full, and that can help fend off post-workout cravings and binges. In fact, research shows that eating small amounts of peanuts can help you maintain a healthy weight. Headed on an easy walk or to yoga class? Half a sandwich may be all you need.
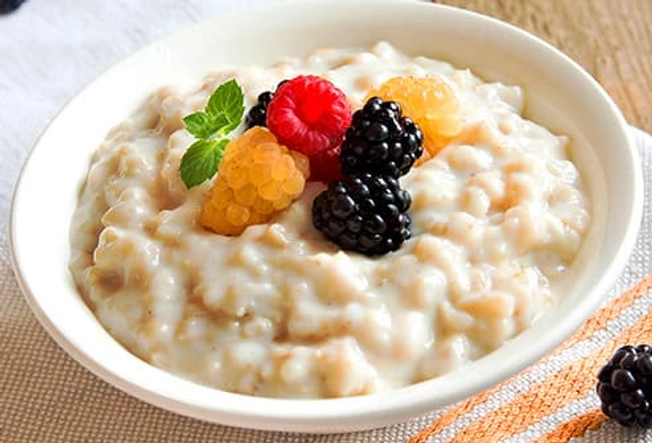

Before: Oatmeal With Low-Fat Milk and Fruit
Do you work out in the morning? Start your day with a bowl of high-fiber, whole grain oatmeal and fruit. Your body digests the carbs in this combo more slowly, so your blood sugar stays steadier. You’ll feel energized for longer. For an extra dose of protein and bone-building calcium, stir in some low-fat milk.
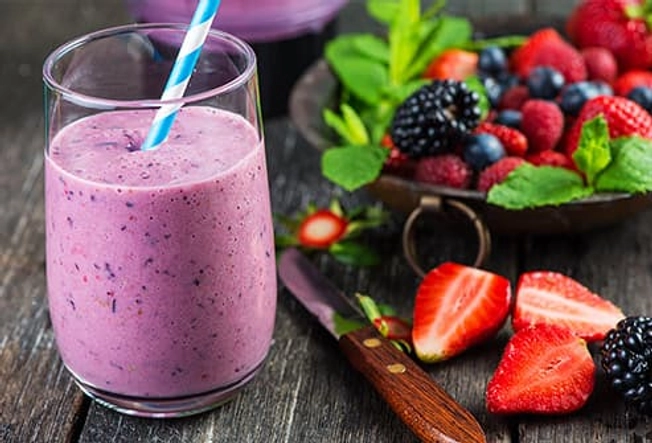

Before: Fruit-and-Yogurt Smoothie
Smoothies are easy to digest, so you won’t feel sluggish during your workout. But many store-bought versions are high in added sugar. Whip up your own version with protein-rich yogurt and fruit, which packs in energy-boosting carbs. Blend it with water or ice to help you stay hydrated. Research shows that not getting enough fluids can zap your strength and endurance.
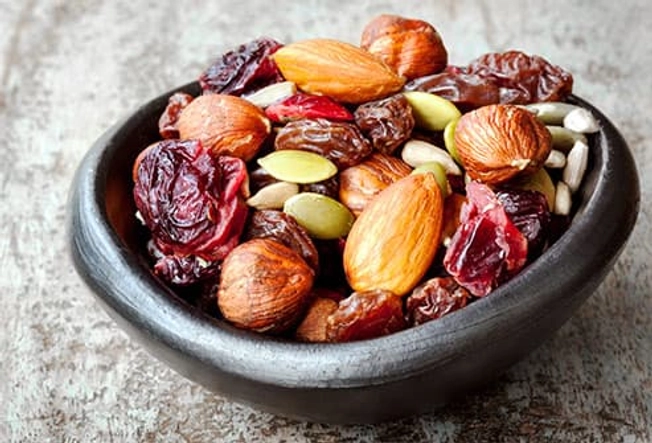

Before: Trail Mix
It’s known as a hiking staple, but trail mix is a good snack for any workout. Raisins give you a quick hit of energy that’s easy on the stomach. Mix a small handful of them with a few almonds, which are high in protein and heart-healthy unsaturated fat. They also have an antioxidant that may help your body use oxygen better -- and give you better exercise results.

Before: Low-Fat Latte and an Apple
If you’re a coffee drinker, sip a latte before that morning or lunchtime fitness class. You’ll get protein from the milk, and the caffeine may ease muscle soreness. Pair it with an apple for high-quality carbs. One warning: Caffeine can mess with your sleep, so avoid it in the afternoon. You could swap the latte for a glass of low-fat milk or piece of string cheese.
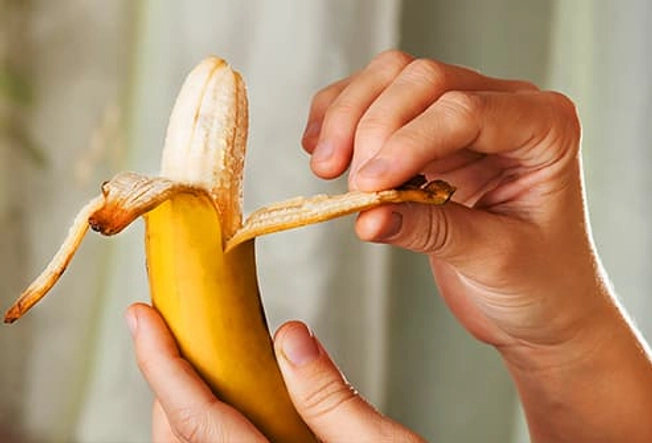

Before: Banana
Only have 5 or 10 minutes before your workout? Snack on a banana. Their easy-to-digest carbs power you up without weighing you down. They’re also a good source of antioxidants and potassium, a mineral that may help prevent muscle cramps. Toss one into your gym bag for a last-minute snack.
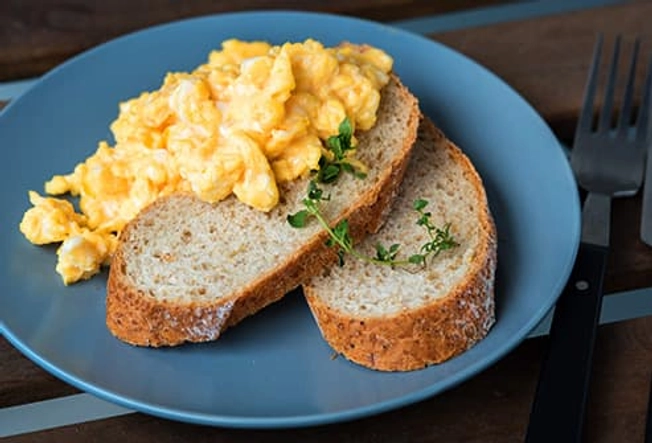

After: Egg and Whole-Wheat Toast
The toast’s carbs put back the energy you burned during exercise, while its fiber keeps your blood sugar levels even. Serve it with an egg to boost your results. They’re a complete protein, which means they have all nine of the essential amino acids your body uses to build muscle. No time for a post-workout scramble? Pack a hard-boiled egg with a whole-grain roll or crackers.
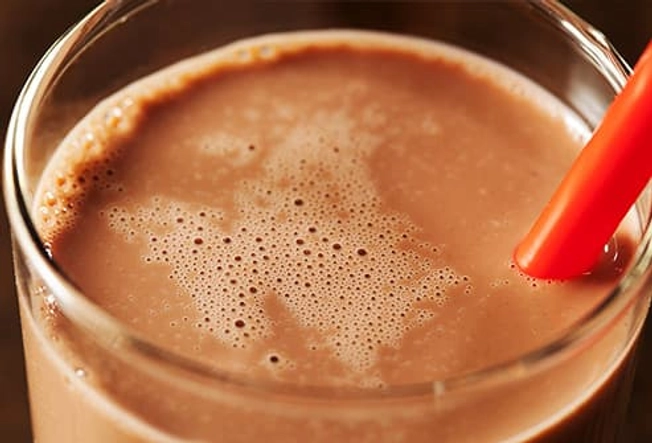

After: Chocolate Milk
This childhood favorite has the ideal ratio of carbs to protein -- about 4 to 1 -- to refuel and rebuild your muscles. One study found that athletes who had a glass after a workout recovered faster than those who had a carb-only sports beverage. Plus, chocolate milk is 90% water, so it replaces some of the fluids you lose during exercise.
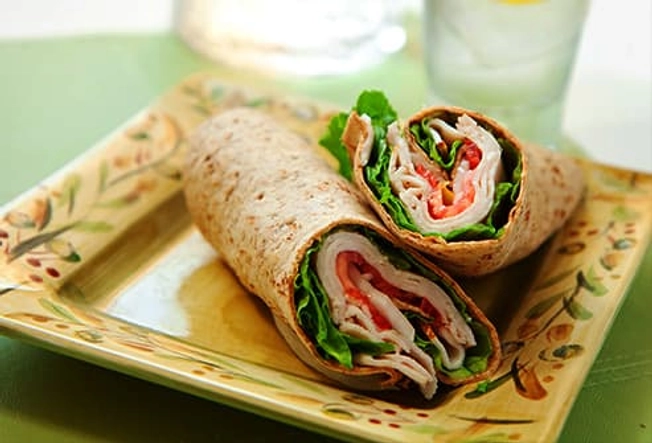

After: Whole-Grain Turkey Wrap
After you wrap up your workout, whip up this easy snack or lunch. The whole grains give you high-fiber carbs, while the turkey has 19 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving. Swap the mayo for creamy avocado -- it’s high in potassium and magnesium, two minerals that can fend off muscle cramps. Bonus: Avocado is also packed with heart-healthy unsaturated fats and plenty of vitamins.
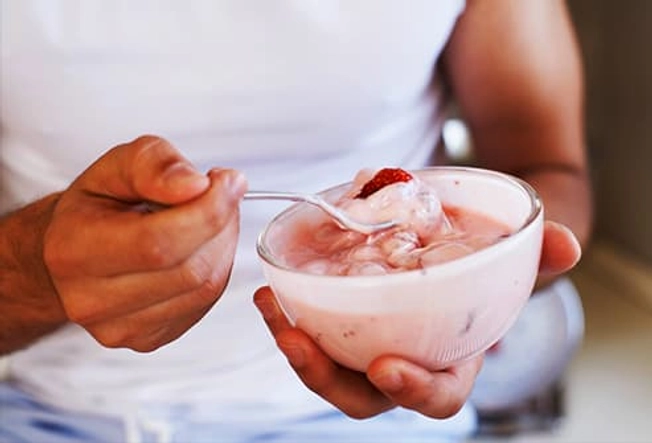

After: Greek Yogurt and Fruit
One cup of this creamy treat offers 20 grams of protein. You can add even more nutrition by topping your bowl with fruit to add energy-boosting carbs. If you use antioxidant-rich blueberries, you’ll get even more benefit. Research shows that eating them after a workout can help with the muscle inflammation brought on by exercise.
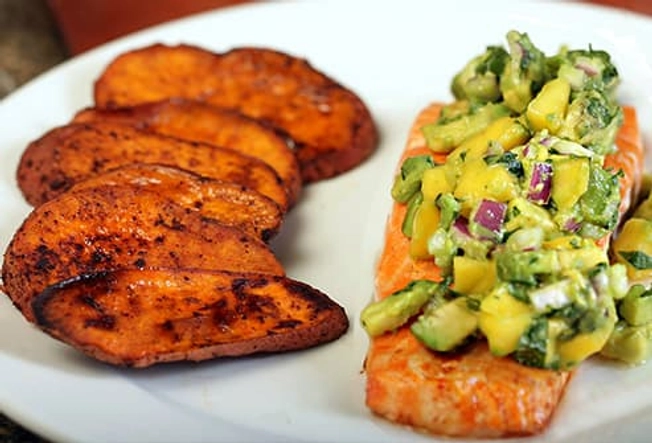
After: Salmon With Sweet Potato
This fish is high in protein and omega-3s -- heart-healthy fats that can ease the post-workout muscle inflammation that causes soreness. Pair salmon with a sweet potato baked in its skin for 23 grams of carbs and 3.8 grams of fiber to keep you full. You’ll also get all the immune-boosting vitamin A you need in a day. Serve your sweet potato roasted or mashed, but skip the high-calorie butter and cream. Use a drizzle of olive oil instead.
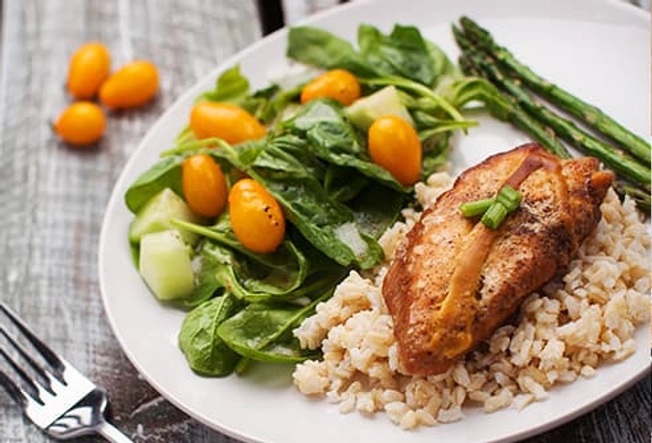

After: Chicken, Brown Rice, and Veggies
There’s a reason skinless chicken breast is thought of as a slim-down food: Half of one packs in 27 grams of protein in only 142 calories. It also has a lot of vitamin B-6, a nutrient important for your immune system. Serve it with brown rice and veggies for the right combination of carbs and nutrients.
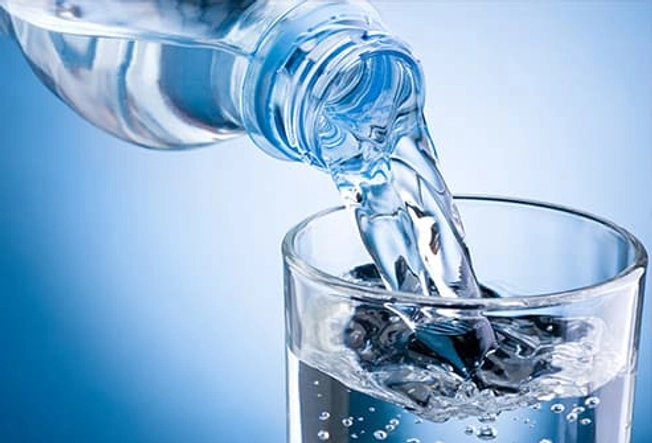

Before, During, and After: Drink Up
Make sure you have plenty of water. How much? Use the following guidelines:
- Before exercise: About 2 to 3 cups
- During exercise: About 1/2 to 1 cup every 15 to 20 minutes
- After exercise: About 2 to 3 cups for every pound you lose during exercise (you can weigh yourself before and after your workout).
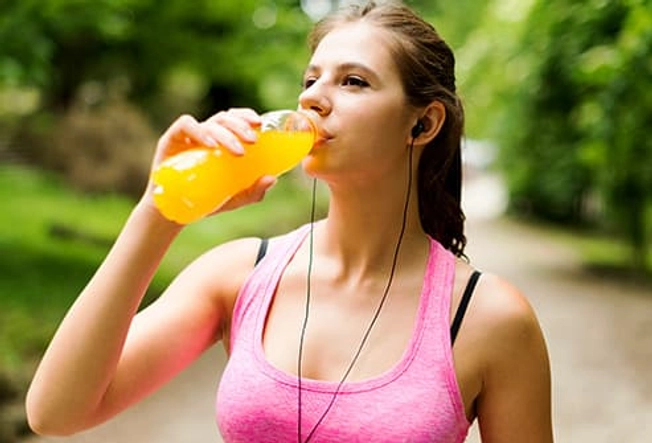

After: Sports Drink?
If you exercise for an hour or less, water is all you need to stay hydrated. But if you go for longer, you need to replace electrolytes. These are minerals, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, that help you stay hydrated. You lose them when you sweat. Look for a drink that has electrolytes, like a sports beverage or coconut water.

Foods to Avoid
Steer clear of rich, greasy foods. Fat takes your body longer to digest, which can lead to an upset stomach. For some people, lots of fiber or protein doesn’t mix with exercise. Every body is different, so pay attention to what works for you. If you’re taking part in a race, such as a 5K, stick with tried-and-true snacks and meals.
